Running pipelines locally
How to run Codefresh pipelines on your workstation
Codefresh can run your pipelines locally. This is very handy when you need to debug a pipeline, or when you want to do quick changes to the codefresh.yml file with the fastest turn-around time possible.
Prerequisites
You need to have Docker installed on your local workstation. You can follow the official instructions to install it. Notice that if you use Linux, the Docker version offered by your native package manager is not always the latest version.
Once docker is installed, check that it runs correctly with:
docker run hello-world
You should get a short welcome message.
TIP
At the time of writing local builds can only run on Linux and Mac workstations. We are working to remove this limitation and allow developers with Windows machines to also run Codefresh pipelines locally.
Then install the open-source Codefresh CLI and set up authentication with your Codefresh account.
Once this is done check that your account is locally accessible by running
codefresh get pipelines
You should see a long list with your pipelines on the terminal output.
Running a pipeline locally
The Codefresh Command Line Interface (CLI) comes with a run parameter that allows you to trigger pipelines externally (outside the Codefresh UI).
Normally, if you run a pipeline this way the CLI will just trigger it remotely (the pipeline itself will still run in the Codefresh infrastructure).
You can pass however the --local option, and this will instruct the CLI to automatically:
- Download the Codefresh build engine locally to your workstation (which itself is a docker image at codefresh/engine)
- Run the build locally using the Codefresh engine on your workstation
- Print all build logs to your terminal
Note that the engine has transparent network access to all the other settings in your Codefresh account and therefore will work exactly the same way as if it was run on Codefresh infrastructure (e.g. use the connected Docker registries you have setup in the UI)
Here is a full example:
codefresh run francisco-codefresh/jan_19/my-basic-pipeline --local -b master -t my-trigger
Keeping the pipeline volume in the local workstation
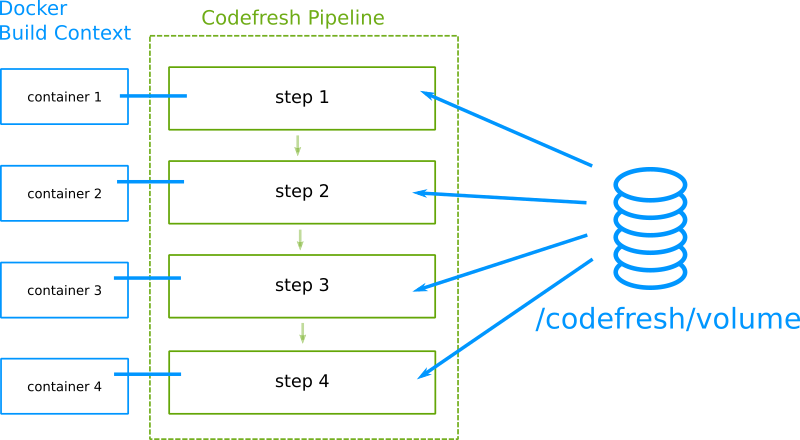
If you are familiar with how Codefresh pipelines work you should know about the unique docker volume that is automatically shared between all pipeline steps.
This volume (which also includes the project folder) makes data sharing between all steps very easy (e.g. with thing such as test reports or binary dependencies).
By default, if you run a Codefresh pipeline locally, this shared volume will automatically be discarded at the end of the build. You can still keep the volume after the build by adding the --local-volume parameter in your run command. Here is an example:
codefresh run francisco-codefresh/jan_19/my-basic-pipeline --local --local-volume -b master -t my-trigger
Once the build runs you will see in your terminal the path that holds the contents of the volume:
[...build logs...]
Using /Users/fcocozza/.Codefresh/francisco-codefresh/jan_19/my-basic-pipeline as a local volume.
[...more build logs]
After the build has finished you can freely explore this folder in your filesystem with any file manager.
$ ls -alh /Users/fcocozza/.Codefresh/francisco-codefresh/jan_19/my-basic-pipeline/
total 16
drwxr-xr-x 5 fcocozza staff 160B Jan 14 12:52 .
drwxr-xr-x 3 fcocozza staff 96B Jan 14 12:52 ..
-rwxr-xr-x 1 fcocozza staff 388B Jan 14 12:52 cf_export
-rw-rw-r-- 1 fcocozza staff 189B Jan 14 12:52 env_vars_to_export
drwxr-xr-x 5 fcocozza staff 160B Jan 14 12:52 jan_19
This way you can verify if the pipeline has access to the data you think it should have
Using a custom codefresh.yml file
The ultimate way to run a pipeline locally is to override completely the codefresh.yml file it uses. A pipeline by default will read its steps from the respective file in git.
You can force it to ignore that git version of the pipeline spec and instead load a custom codefresh.yml from your local file-system (which might not be even committed yet).
The extra parameter is --yaml in that case.
Here is a complete example
codefresh run francisco-codefresh/jan_19/my-basic-pipeline --local --local-volume --yaml=my-codefresh.yml -b master -t my-trigger
When this pipeline runs locally, it will use whatever steps exist in my-codefresh.yml instead of the git version. The shared data volume will also be left intact after the build is finished as explained in the previous section.