Managing external clusters in GitOps Runtimes
Add multiple remote clusters to a GitOps Runtime and deploy applications
Once you have an Argo CD installation as part of a Hybrid GitOps Runtime, you can add external clusters to them. You can then deploy applications to those clusters without having to install Argo CD on the clusters in order to do so.
When you add an external cluster to a provisioned GitOps Runtime, the cluster is registered as a managed cluster. A managed cluster is treated as any other managed K8s resource, meaning that you can monitor its health and sync status, deploy applications to it, view information in the Applications dashboard, and remove the cluster from the Runtime’s managed list.
Adding a managed cluster via Codefresh ensures that Codefresh applies the required RBAC resources (ServiceAccount, ClusterRole and ClusterRoleBinding) to the target cluster, creates a Job that updates the selected Runtime with the information, registers the cluster in Argo CD as a managed cluster, and updates the platform with the new cluster information.
Prerequisites
- Valid Git user token with the required scopes
- Latest version of the Codefresh CLI
- Codefresh token in user settings
- The following permissions in the Managed Cluster:
ClusterRole(create)ClusterRoleBinding(create)ConfigMap(create,get)Job(create)Secret(create,get)ServiceAccount(create,get,patch)
- For ingress-based GitOps Runtimes, the ingress host of the Runtime (use
cf runtime listto get this).
Adding managed clusters
Add a managed cluster in any of the following ways:
Add a managed cluster in Codefresh
Add an external cluster to a provisioned GitOps Runtime in the Codefresh UI. When adding the cluster, you can also add labels and annotations to the cluster, which are added to the cluster secret created by Argo CD.
Optionally, to first generate the YAML manifests, and then manually apply them, use the dry-run flag in the CLI.
How to
- In the Codefresh UI, on the toolbar, click the Settings icon.
- From Runtimes in the sidebar, select GitOps Runtimes.
- From either the Topology or List views, select the Runtime to which to add the cluster.
- Topology View: Select
 .
List View: Select the Managed Clusters tab, and then select + Add Cluster.
.
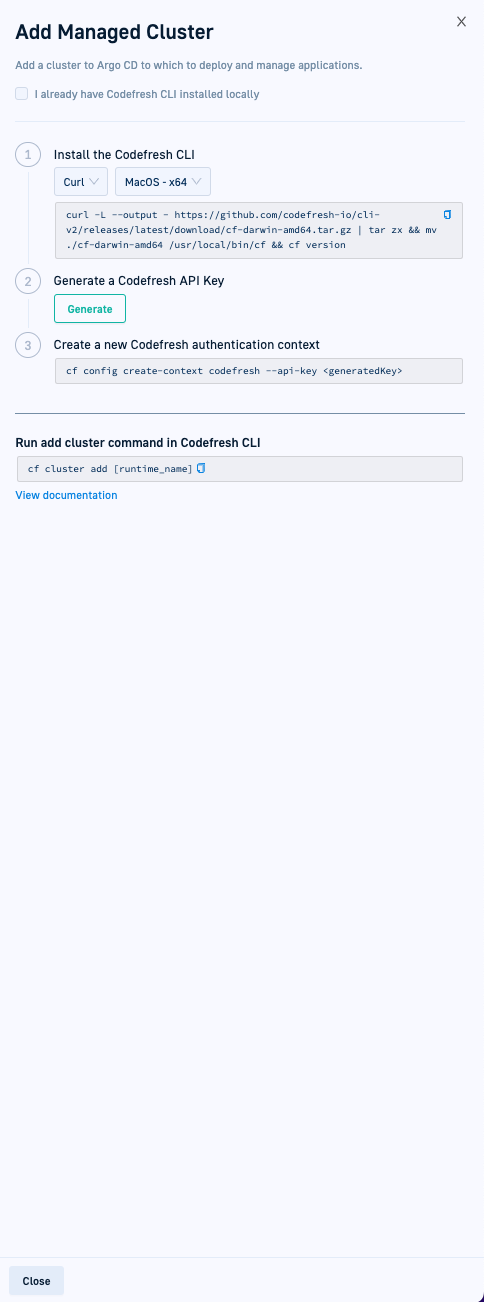
List View: Select the Managed Clusters tab, and then select + Add Cluster. - In the Add Managed Cluster panel, if needed install the Codefresh GitOps CLI.
- Copy and run the command:
cf cluster add [runtime-name] [--labels label-key=label-value] [--annotations annotation-key=annotation-value][--dry-run]where:runtime-nameis the name of the Runtime to which to add the cluster.--labelsis optional, and required to add labels to the cluster. When defined, add a label in the formatlabel-key=label-value. Separate multiple labels withcommas.--annotationsis optional, and required to add annotations to the cluster. When defined, add an annotation in the formatannotation-key=annotation-value. Separate multiple annotations withcommas.--dry-runis optional, and required if you want to generate a list of YAML manifests that you can redirect and apply manually withkubectl.
- If you used
dry-run, apply the generated manifests to the same target cluster on which you ran the command. Here is an example of the YAML manifest generated with the--dry-runflag. Note that the example has placeholders, which are replaced with the actual values during the--dry-run.
The new cluster is registered to the GitOps Runtime as a managed cluster.
Add a managed cluster with Kustomize
- Locally clone https://github.com/codefresh-io/csdp-official/tree/main/add-cluster/kustomize.
- Update
configmap.ymlandsecret.ymlwith the requires values. - Run
kustomize buildorkubectl -kto apply the final result to the cluster.
NOTE
For ingress-based GitOps Runtimes, to get theingressUrlfor your, first authenticate to the Codefresh GitOps CLI, and then runcf runtime listin your terminal.
Add a managed cluster with Helm
The Helm chart is published at oci://quay.io/codefresh/charts/csdp-add-cluster. You can see the source templates at https://github.com/codefresh-io/csdp-official/tree/main/add-cluster/helm.
To deploy the chart:
- Copy the values.yaml file locally.
- Fill in the required values.
- Run:
helm install oci://quay.io/codefresh/charts/csdp-add-cluster -f values.yaml --generate-name
NOTES
- For ingress-based GitOps Runtimes, to get the
ingressUrlfor your Runtime, first authenticate to the GitOps CLI, and then runcf runtime listin your terminal.- The Helm Chart is installed by default in the
kube-systemnamespace. To change the namespace, configure thesystemNamespacevalue in addition to the--namespaceoption, so both the Helm Release and the resources are installed in the desired namespace.
Add a managed cluster with Terraform
- Use the Helm provider as any other Helm chart.
resource "helm_release" "my-managed-cluster" {
name = "my-managed-cluster"
repository = "oci://quay.io/codefresh/charts"
chart = "csdp-add-cluster"
values = [
"${file("values.yaml")}"
]
}
- Apply the file using Terraform or your favorite workflow tool.
View managed clusters
View managed clusters in either the Topology or List Runtime views. For information on Runtime views, see Runtime views. As the cluster is managed through the Runtime, updates to the Runtime automatically updates the components on all the managed clusters that include it.
View connection status for the managed cluster, and health and sync errors. Health and sync errors are flagged by the error notification in the toolbar, and visually flagged in the List and Topology views.
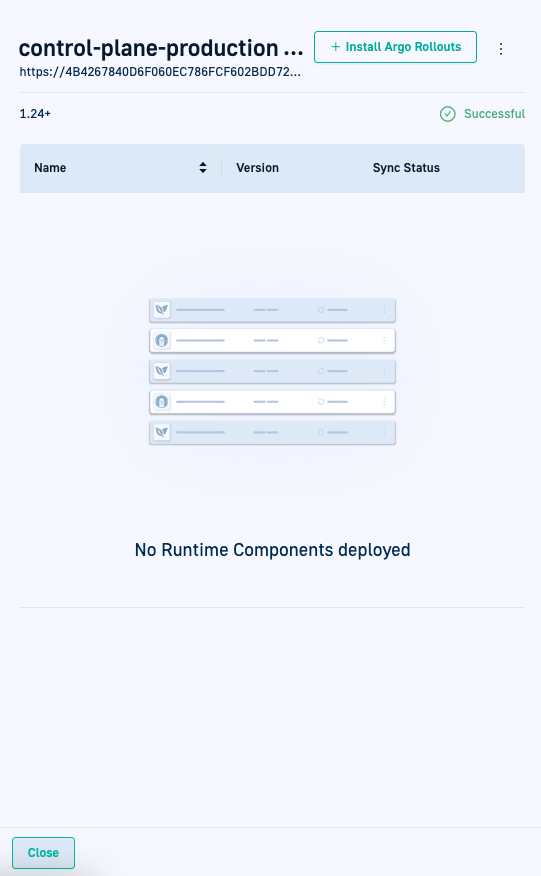
Install Argo Rollouts
Applications with rollout resources need Argo Rollouts on the target cluster, both to visualize rollouts in the GitOps Apps dashboard, and control rollouts with the Rollout Player.
If Argo Rollouts has not been installed on the target cluster, the Install Argo Rollouts button is displayed.
Install Argo Rollouts with a single click to execute rollout instructions, deploy the application, and visualize rollout progress in the GitOps Apps dashboard.
- In the Codefresh UI, on the toolbar, click the Settings icon, and from Runtimes in the sidebar, select GitOps Runtimes.
- Select Topology View.
- Select the target cluster, and then select + Install Argo Rollouts.
Removing managed clusters
Removing a cluster as a deployment target means removing it from the GitOps Runtime that manages it.
NOTE
This action only removes the management link between your GitOps Runtime and your cluster. Applications that are already running on the cluster are not affected.
Remove a managed cluster in any of the following ways:
Remove a managed cluster from the Codefresh UI
Remove a cluster from a GitOps Runtime through the Codefresh UI.
TIP
You can also remove it through the CLI.
In the Codefresh UI, on the toolbar, click the Settings icon, expand Runtimes in the sidebar, and select GitOps Runtimes.
- Select either the Topology View or the List View tabs.
- Do one of the following:
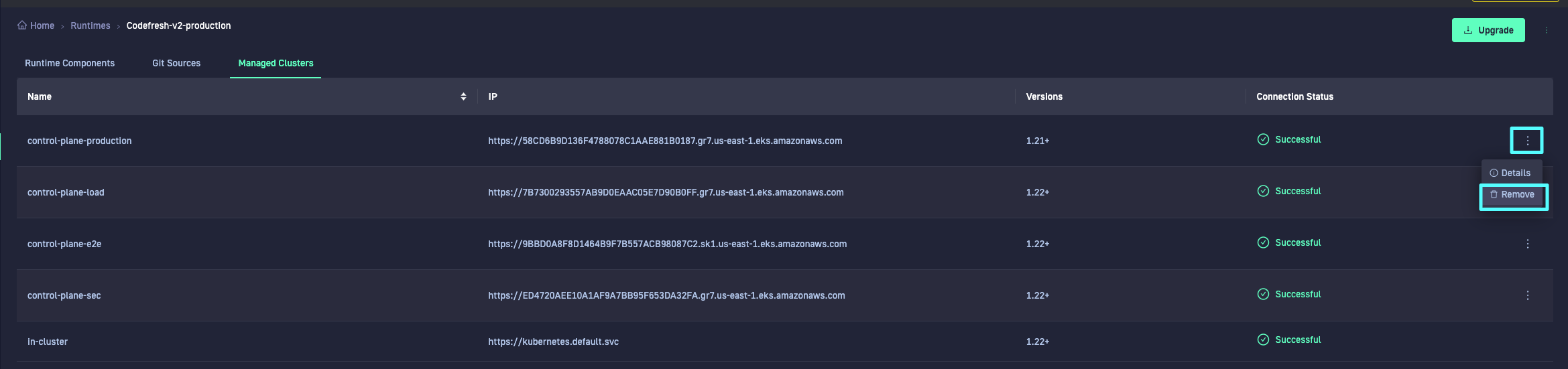
- In the Topology View, select the cluster node from the Runtime it is registered to.
- In the List View, select the Runtime, and then select the Managed Clusters tab.
- Select the three dots next to the cluster name, and then select Uninstall (Topology View) or Remove (List View).
Remove a managed cluster through the GitOps CLI
Remove a managed cluster from the GitOps Runtime through the GitOps CLI.
NOTE
Run the command on the cluster you want to remove.
- Run:
cf cluster remove <runtime-name> --server-url <server-url>where:<runtime-name>is the name of the GitOps Runtime that the managed cluster is registered to.<server-url>is the URL of the server on which the managed cluster is installed.
Remove a managed cluster with Terraform
Use the terraform destroy command.
Related articles
Managing Git Sources in GitOps Runtimes
Monitoring GitOps Runtimes
Managing GitOps Runtimes