Shared configuration for pipelines
How to keep your pipelines DRY
After creating several pipelines in Codefresh, you will start to notice several common values between them. Common examples are access tokens, environment URLs, configuration properties etc.
Codefresh allows you to create those shared values in a central place and then reuse them in your pipelines avoiding the use of copy-paste.
You can share:
- Environment parameters (easy)
- Helm values (easy)
- Any kind of YAML data (advanced)
Creating shared configuration contexts
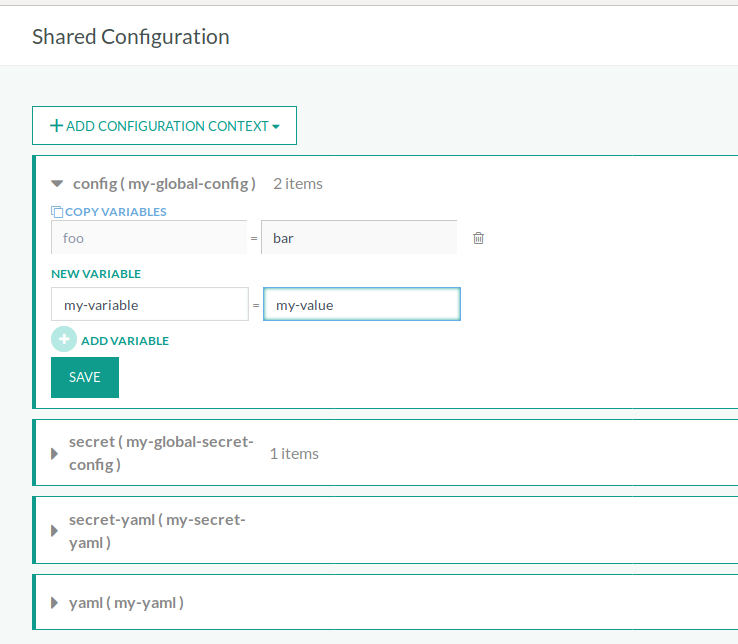
Create one or more shared configuration contexts at the account-level to use in pipelines.
- In the Codefresh UI, on the toolbar, click the Settings icon.
- From the sidebar, select Shared Configuration.
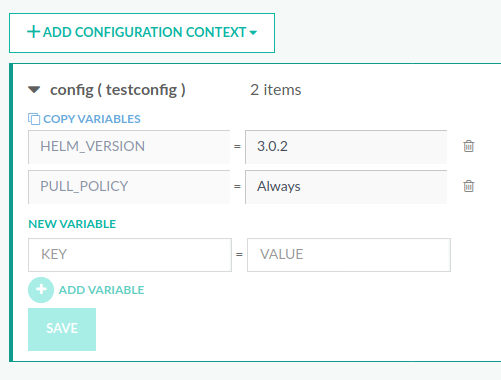
- Click Add Configuration Context and select the type of shared configuration context to add.
- Enter a name for the shared configuration context and click Save.
- Add one or more variables in Key = Value format.
- To allow access to all users, toggle Allow access to all users ON.
- Click Save.
You can create four types of shared configuration contexts:
- Shared Configuration: for environment variables
- Shared Secret: for encrypted environment variables of sensitive data (access tokens, etc.)
- YAML: for Helm values or any other generic information
- Secret YAML: for above, but encrypts the contents
NOTE
RBAC is supported for all types of shared configurations.
You can create as many shared snippets as you want (with unique names).
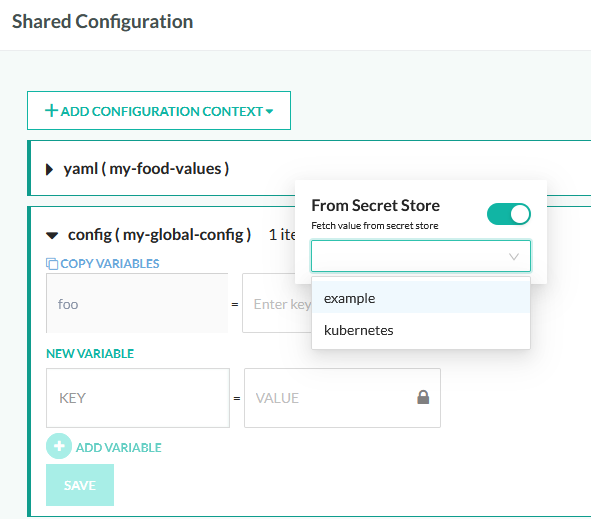
Using external secrets as values
Note that the default “shared secrets” and “secret yaml” entities use the built-in secret storage of Codefresh. You can also use any external secrets that you have defined (such as Kubernetes secrets), by using the normal entities and then clicking on the lock icon that appears.
If you have already specified the resource field during secret definition the just enter on the text field the name of the secret directly, i.e. my-secret-key.
If you didn’t include a resource name during secret creation then enter the full name in the field like my-secret-resource@my-secret-key.
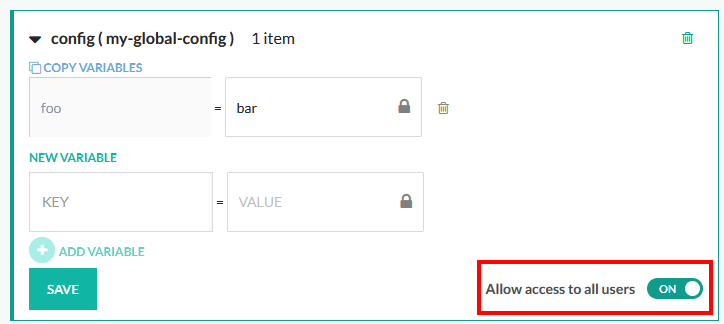
Level of access
For each set of values you can toggle the level of access by non-admin users. If it is off, users will not be able to use the CLI or API to access these values. If it is on, all users from all your Codefresh teams will be able to access this set of values with CLI commands or API calls.
We recommend that you disable access for all values of type shared secret and secret YAML unless your organization has different needs.
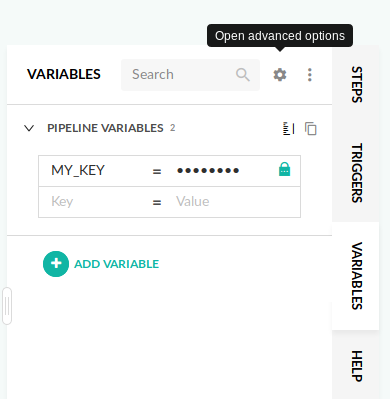
Using shared environment variables
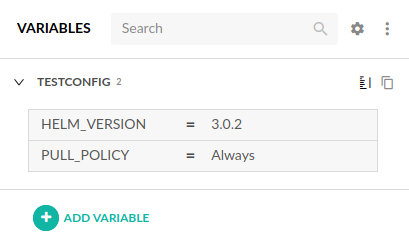
Each pipeline has a set of environment variables that can be defined in the Workflow screen. To import a shared configuration open the pipeline editor, and from the tabs on the right side select VARIABLES. Then click the gear icon to Open Advanced Options:
To use your shared configuration, click the Import from shared configuration button and select the snippet from the list:
Once you click Add the values from the shared configuration will be appended to the ones you have in your pipelines. In case of similar values the shared configuration will follow the precedence rules.
Using shared Helm values
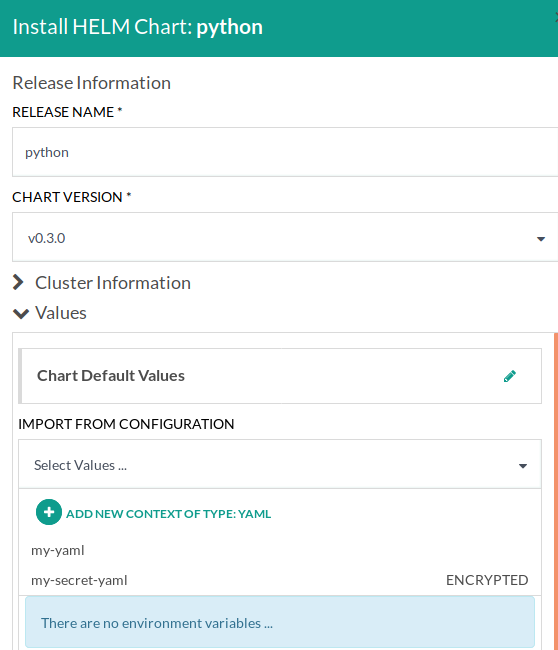
To use a shared YAML snippet for Helm values you can install a new Helm chart either from the:
In both cases, when you see the Helm installation dialog you can import any of your YAML snippets to override the default chart values.
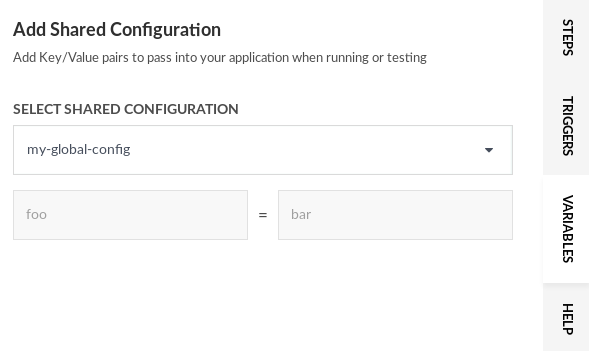
From the same dialog you can also create a brand-new shared configuration snippet of type YAML. Not only it will be used for this Helm chart, but it will be added in your global shared configuration as well.
Using values from the Shared Configuration in your Helm step
Additionally, you can define shared variables in your account settings and reuse those across your Helm steps, and specifically, in your custom Helm values.
Under Account Setting > Shared Configuration, add the variable to your shared configuration.
Go to the workflow of the Codefresh pipeline to which you want to add the variable. Then select variables from the right sidebar. Open advanced configuration and select Import from shared configuration.
This will allow you to add shared variables.
Add the shared variables to your Helm step:
deploy:
type: "helm:1.1.12"
working_directory: "./react-article-display"
stage: "deploy"
arguments:
action: "install"
chart_name: "charts/example-chart"
release_name: "test-chart"
helm_version: "${{HELM_VERSION}}"
kube_context: "anais-cluster@codefresh-sa"
custom_values:
- 'pullPolicy=${{PULL_POLICY}}'The shared variables can now be used across your pipelines.
Sharing any kind of YAML data in pipelines
All the snippets from shared configuration are also available as context in the Codefresh CLI.
This means that you can manipulate them programmatically and read their values in the pipeline in any way you see fit.
If for example you have a shared configuration named my-global-config you can easily read its contents programmatically using the CLI:
$codefresh get context my-global-config --output=yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: context
metadata:
default: false
system: false
name: my-global-config
type: config
spec:
type: config
data:
foo: barExample - custom value manipulation
Let’s say that you have a YAML segment with the following content:
favorite:
drink: coffee
food: pizzaHere is a pipeline step that reads the YAML snippet and extracts a value:
YAML
version: '1.0'
steps:
MyFavoriteFoodStep:
title: Favorite food
image: codefresh/cli
commands:
- echo I love eating $(codefresh get context my-food-values --output=json | jq -r '.spec.data.favorite.food')Once the pipeline runs, you will see in the logs:
I love eating pizza
Manipulating shared configuration programmatically
You can also manipulate shared configurations programmatically via the Codefresh CLI and the Codefresh API.
For example, you can reference one or more shared configuration contexts directly in the YAML using spec.contexts as described below.
If you have a shared configuration named test-hello that includes the variable test=hello, you can add spec.contexts.test-hello to the pipeline YAML, and then reference this variable in the pipeline as you would any other variable.
version: "1.0"
kind: pipeline
metadata:
name: default/test-shared-config-from-pipe-spec
spec:
contexts:
- test-hello
steps:
test:
image: alpine
commands:
- echo ${{test}} # should output "hello"For detailed information on how to create/update/delete shared configuration contexts via the CLI, see Contexts.
For information on all the options available in the full Codefresh YAML, see Full pipeline specifications.
Related articles
Variables
Codefresh YAML for pipeline definitions
Pipeline steps