Secret Storage integrations
Manage Kubernetes secrets with Codefresh
Codefresh can resolve variables storing secrets from remote sources. This allows you to keep sensitive data on your cluster, and for Codefresh to request it during pipeline execution on-demand.
Secret-Store is an additional context in Codefresh. Codefresh supports two types of secret storage:
- Kubernetes secrets for SaaS versions
- Runtime-Kubernetes for hybrid deployments with Codefresh Runner
You can set up both types either in the Codefresh UI or via the CLI (codefresh create context secret-store --help).
NOTE
This feature is for Enterprise accounts only.
Kubernetes secret store setup
Kubernetes the native secrets supported by a cluster.
Prerequisites
- For the Kubernetes secret store, connect your Kubernetes cluster to Codefresh.
- Create a Kubernetes secret:
Create a Kubernetes Secret
Create your secret in Kubernetes:
kubectl create secret generic my-secret --from-literal=key1=supersecret
kubectl create configmap my-config-map --from-literal=key1=config1
Set up Kubernetes secret integration in Codefresh UI
IMPORTANT
The name assigned to the integration must be unique within the account. Using the same name for other integrations or Shared Configuration contexts within pipelines will result in conflicts.
For troubleshooting, see Error: context already exists.
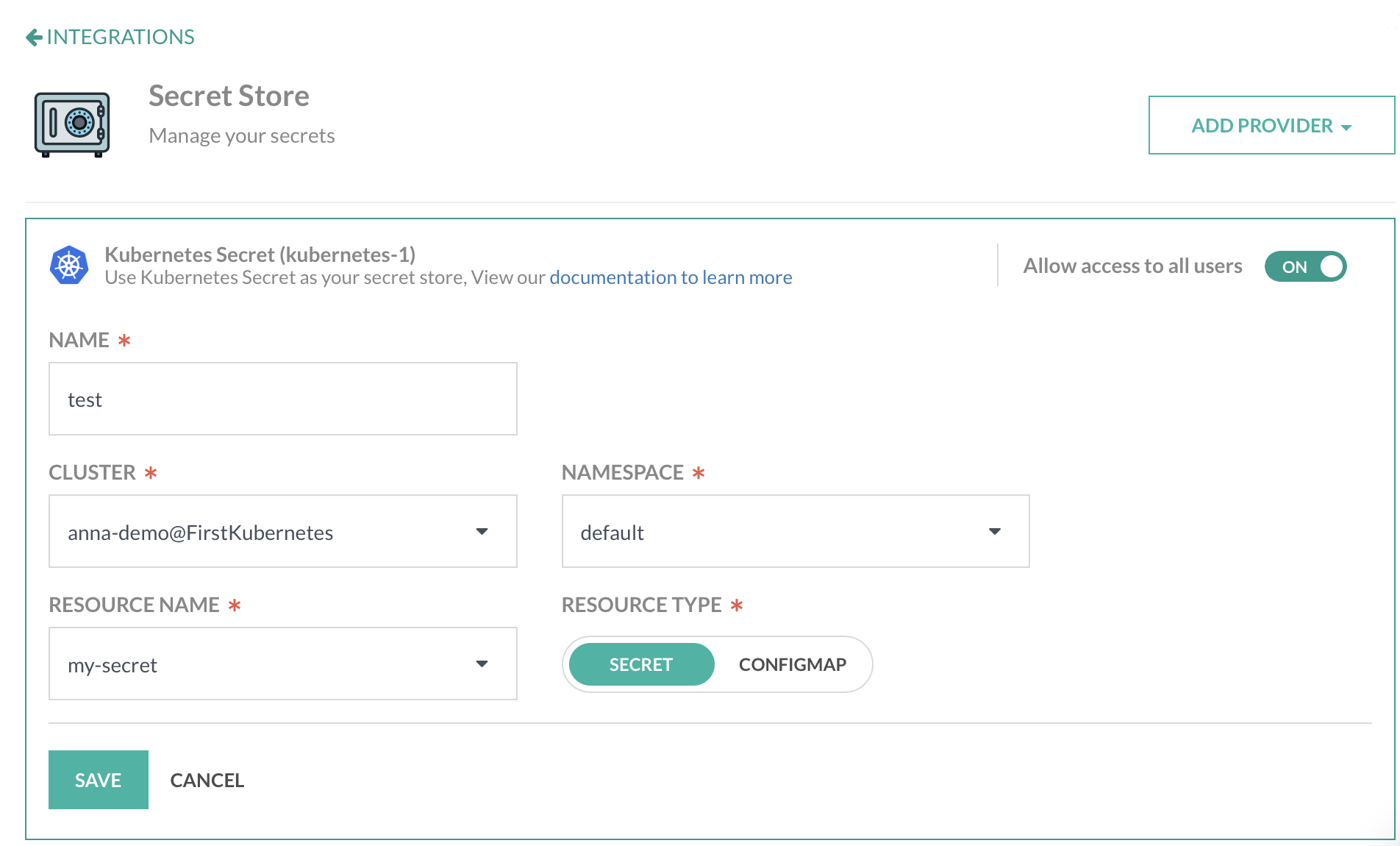
- In the Codefresh UI, on the toolbar, click the Settings icon, and then from the sidebar, select Pipeline Integrations.
- Select Secret Store and then click Configure.
- From the Add Provider dropdown, select Kubernetes.
- Do the following:
- Name: A unique name given to your context, which will be referenced in
codefresh.yaml. - Resource Type: Select Secret and the data is base64 decoded during resolution.
- Cluster: The name of the cluster as it is configured in Codefresh.
- Namespace: The namespace where the secret is stored.
- Resource Name: Optional. The name of the secret.
- To allow all users in the account access to the secret, enable Allow access to all users.
- Name: A unique name given to your context, which will be referenced in
- To apply the changes, click Save.
Set up Kubernetes secret integration via Codefresh CLI
- To create a secret store context for Kubernetes, run:
codefresh create context secret-store kubernetes "$NAME_IN_CODEFRESH" --cluster "$CLUSTER" --namespace "$NAMESPACE" --resource-type "$TYPE" --resource-name ”$NAME”OR, for our example:
codefresh create context secret-store kubernetes "test" --cluster "anna-demo@FirstKubernetes" --namespace "default" --resource-type secret --resource-name "my-secret"
where:
$NAME_IN_CODEFRESHis a unique name given to your context, which will be referenced incodefresh.yamllater.$CLUSTERis the name of the cluster as it is configured in Codefresh.$NAMESPACEis the Kubernetes namespace where the secret is stored.$TYPEis of eithersecretorconfigmap- if
secret, data will be base64 decoded during resolution - if
configmap, data will be replaced as is
- if
$RESOURCE_NAMEis optional and is the name of the secret
Secret store setup for Codefresh Runner installation
For Codefresh Runner installations, you can also store secrets in your own runtime.
Set up runtime secret store in Codefresh UI
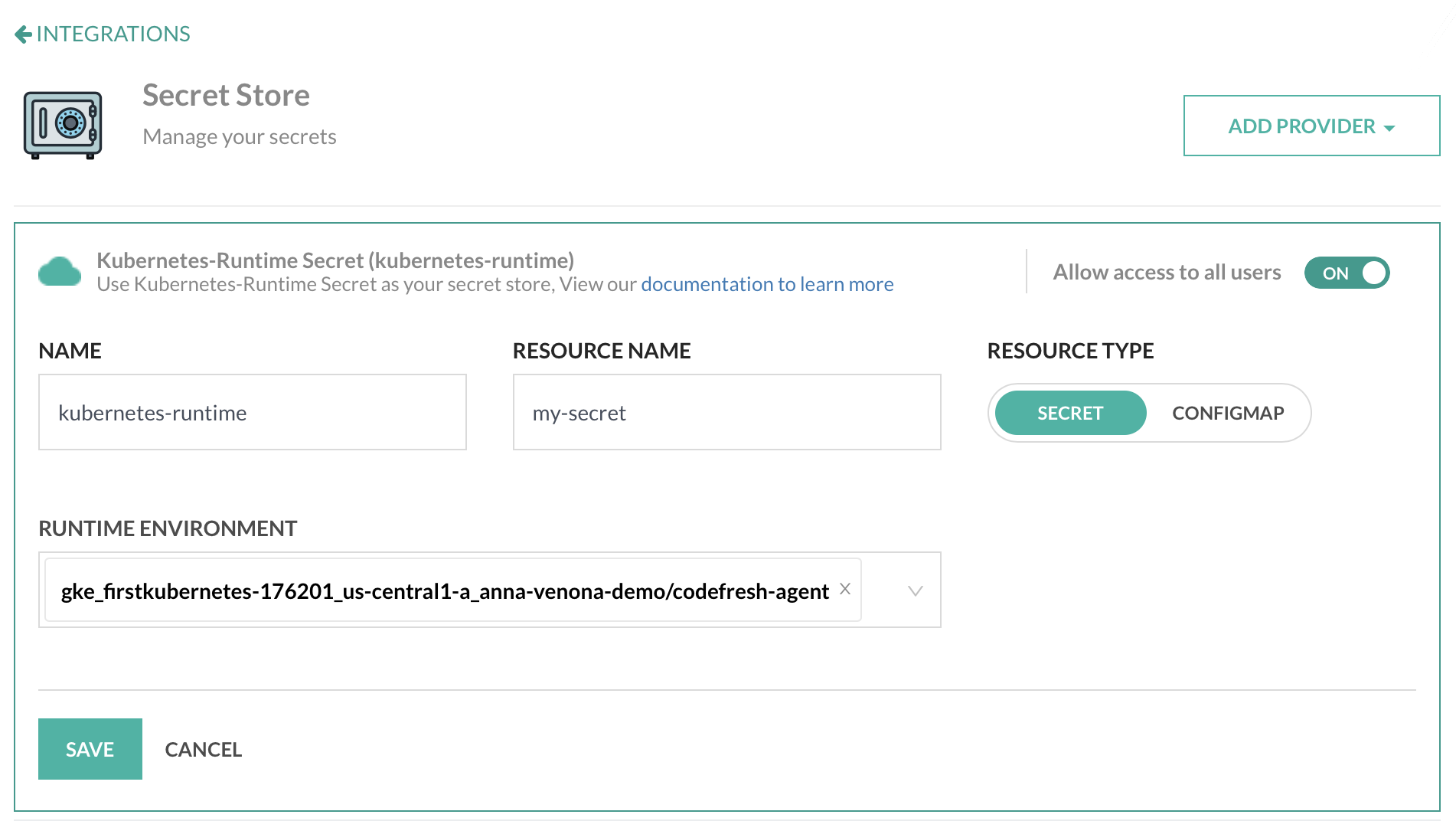
- In the Codefresh UI, on the toolbar, click the Settings icon, and then from the sidebar, select Pipeline Integrations.
- Select Secret Store and then click Configure.
- From the Add Provider dropdown, select Runtime secret.
- Do the following:
- Name: A unique name given to your context, which will be referenced in
codefresh.yaml. - Resource Name: The name of the secret.
- Resource Type: Select the type of secret . - if
secret, data will be base64 decoded during resolution - if
configmap, data will be replaced as is - Runtime Environment: Select the runtime environment with the secret.
- To allow all users in the account access to the secret, enable Allow access to all users.
- Name: A unique name given to your context, which will be referenced in
- To apply the changes, click Save.
Set up runtime secret store with Codefresh CLI
To create a secret store context for Runtime-Kubernetes environments (behind the firewall), run:
codefresh create context secret-store kubernetes-runtime "$NAME_IN_CODEFRESH" --runtime "$RUNTIME_NAME" --resource-type "$TYPE" --resource-name ”$NAME”
or, for our example:
codefresh create context secret-store kubernetes-runtime "test" --runtime "gke_firstkubernetes-176201_us-central1-a_anna-demo" --resource-type secret --resource-name "my-secret"
where:
$NAME_IN_CODEFRESHis a unique name given to your context, which will be referenced incodefresh.yamllater.$CLUSTERis the name of the cluster as it is configured in Codefresh$NAMESPACEis the Kubernetes namespace$TYPEis of eithersecretorconfigmap- if
secret, data will be base64 decoded during resolution - if
configmap, data will be replaced as is
- if
$RESOURCE_NAMEis the name of the secret (optional)$RUNTIME_NAMEis the name of the run-time environment to be configured as secret store. If not set, any runtime-environment will be considered.
Using the secrets
Once Codefresh is linked to your secrets, you can use them either in pipelines or any relevant section in the Codefresh UI. For details, see Using secrets.
Related articles
Shared Configuration
Git integration for pipelines
Kubernetes integration for pipelines
Container registry integration for pipelines