Compile and package an Android application
Using Codefresh pipelines
Android applications use Java/Gradle for their build system. Because Codefresh already supports Gradle, it is also very easy to build Android projects.
Any Gradle command can run inside a Docker image that contains the Android SDK. As an example, we will use a Nextcloud image from Dockerhub.
The example project
You can see the example project at https://github.com/codefresh-contrib/android-sample-app. The repository contains a Hello World Android project with the following tasks:
./gradlew testruns unit tests./gradlew buildbuilds the application
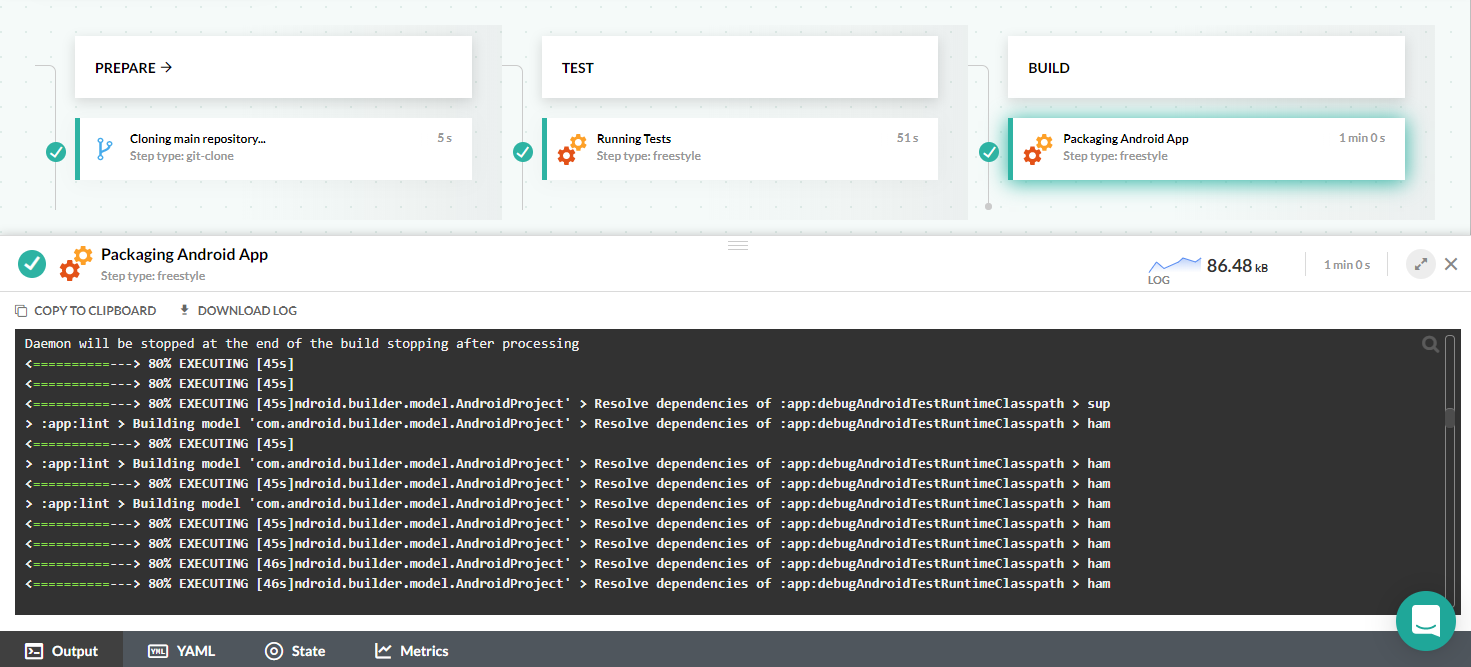
Create a CI pipeline that compiles/releases Android
In most cases you would create a similar pipeline to a Gradle project.
Here is the full pipeline that uses a Docker image with the Android SDK in order to run Gradle.
codefresh.yml
version: '1.0'
stages:
- prepare
- test
- build
steps:
main_clone:
title: Cloning main repository...
stage: prepare
type: git-clone
repo: 'codefresh-contrib/android-sample-app'
revision: master
git: github
TestIt:
title: Running Tests
stage: test
image: nextcloudci/android:android-48
commands:
- chmod +x ./gradlew
- ./gradlew test --no-daemon --gradle-user-home=/codefresh/volume/.gradle
BuildIt:
title: Packaging Android App
stage: build
image: nextcloudci/android:android-48
commands:
- ./gradlew build --no-daemon --gradle-user-home=/codefresh/volume/.gradleThis pipeline clones the source code, runs unit tests and finally builds the Android application.
Codefresh is smart enough that caches automatically for us the workspace of a build (/codefresh/volume). This works great for build tools that keep their cache in the project folder, but not for Maven/Gradle which keep their cache externally. By changing the location of the Gradle cache we make sure that Codefresh will cache automatically the Gradle libraries resulting in much faster builds.
Related articles
Codefresh YAML for pipeline definitions
Steps in pipelines
Creating pipelines
How Codefresh pipelines work