Configuring version and promotable properties for products
Configure application version and properties to promote for products
Application version and promotable properties for products
By default, when you promote a product across environments, all its applications and their properties are promoted. Not all properties change with every update, and different environments have different requirements. For example, while development environments may allow frequent updates, staging and production environments often require stricter controls.
By configuring which properties to promote, you ensure that only relevant updates move forward. This improves deployment accuracy, streamlines workflows, and enforces compliance with environment-specific constraints. Manual reviews and oversight are reduced for managing complex applications.
Key benefits of automated selection
-
Targeted, reliable promotions
Ensures only approved updates, such as tested builds and specific artifact versions are promoted, minimizing deployment errors. -
Environment-specific control
Defines promotable properties to enforce unique requirements per environment, allowing selective updates like image tags while excluding unnecessary modifications. -
Scalability for complex applications
Eliminates manual diff reviews for large-scale applications with numerous microservices and configuration files, streamlining deployments.
Primary aspects when promoting applications
When defining which changes to promote, focus on these two aspects:
- Defining the source for the application’s release version
- Defining the changes to promote across multiple files in the applications
IMPORTANT
For automated retrieval of the application version and promotion of specific attributes from files across environments, all applications within the same product must maintain an identical structure.
Promotion across different environments requires consistent relative paths in each repository. For example, to promote properties from config/settings.yaml in environment dev to testing, config/settings.yaml must also exist in the testing environment.
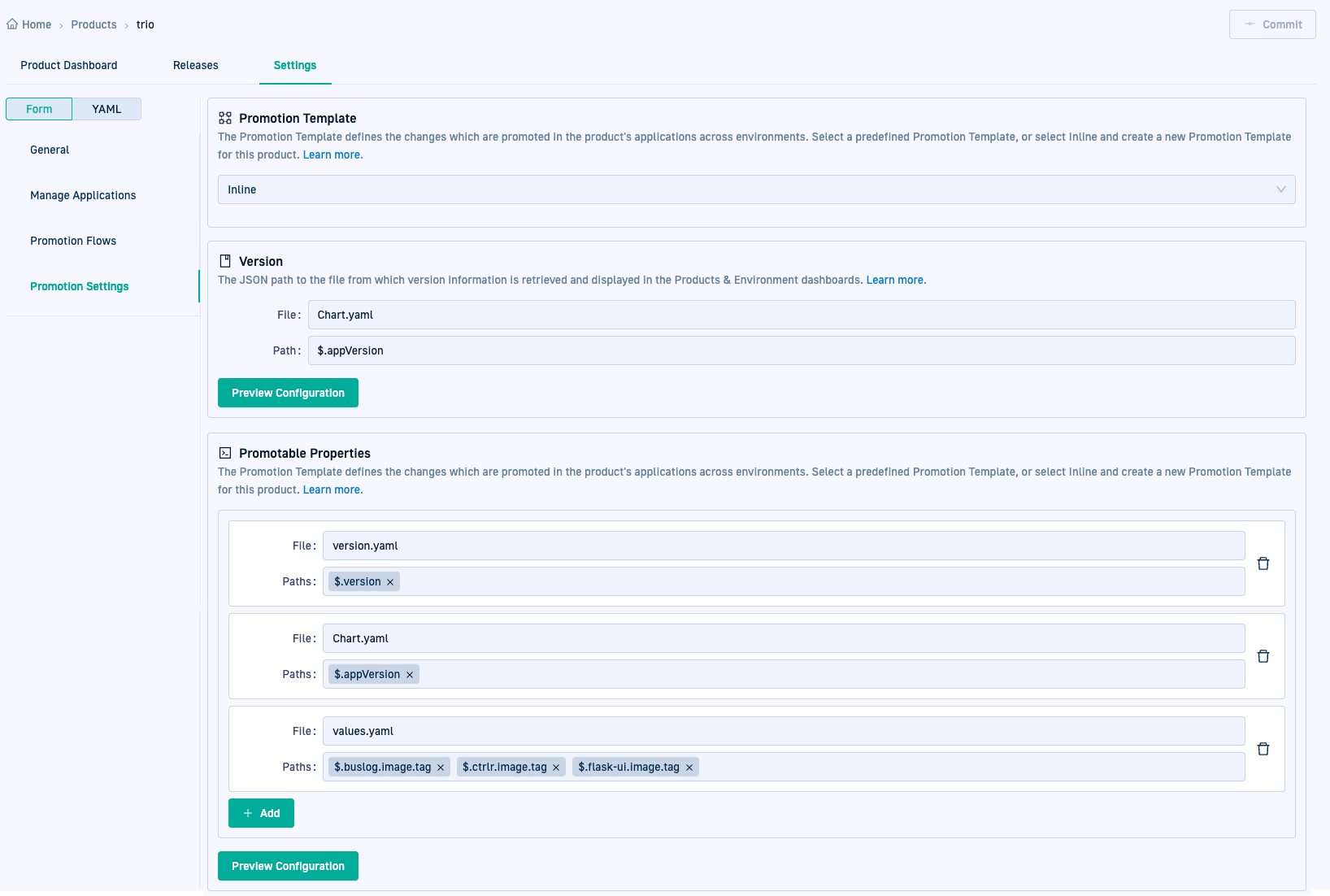
Where to configure settings for application version and properties
In Product > Settings > Promotion Settings.
See also Promotion Settings & Promotion Templates.
For how-to instructions, see Configure Promotion Settings.
Configuring versions for promoted applications
The Version attribute specifies the location from which to retrieve version information for the applications in the product.
NOTE The Environments, Product, and GitOps Apps dashboards display the product version only for Helm application types. For other application types, product versions are not displayed even when configured.
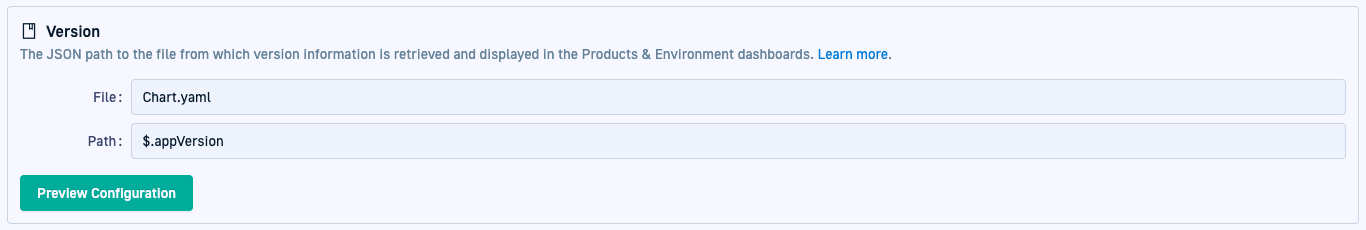
The Version attribute is defined using a JSON path expression. It is relative to the spec.source.repoURL and spec.source.path attributes defined in the source application’s configuration manifest.
The following diagram illustrates how the version attributes configured for a product correlate with the repo URL and path defined in the application’s manifest to retrieve the correct version.
Application version not updated/displayed in dashboards
- There are no updates in the application. The application version updates only when the application itself is updated, not just by changing the version number.
- If the version is not displayed in the dashboards, it could be because your application is not a Helm application.
- For Helm applications, if the version is either not displayed or is not correct, it could be because:
- Codefresh could not find the values in the
repoURLandpath. Verify that the Source settings for the application correspond to the Version attribute configured for the product. - The JSON key includes a dash character which is not supported. See Dashes in JSON keys.
- Codefresh could not find the values in the
Examples of version attributes
You can extract version information from different attributes to ensure that it aligns with your deployment and business requirements.
| Version attribute | Example configuration | JSON Path expression | Possible use case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Default version attribute | |
$.appVersion |
Commonly used in Helm charts or deployment manifests for explicit version management. |
| Semantic versioning | |
$.version |
Indicate backward-compatible changes, new features, and bug fixes. |
| Image tag | |
$.image.tag |
In containerized environments to manage versions tied to Docker images. |
| Git commit SHA | |
$.git.commitSha |
Track versions using specific Git commit SHAs, useful in CI/CD pipelines. |
| Build number | |
$.build.number |
Include timestamps or incremental identifiers automatically generated during builds. |
| Release version | |
$.release.version |
Differentiate between stages of software maturity and deployment readiness (e.g., alpha, beta, production). |
| Deployment version | |
$.deployment.version |
Manage versioning per deployment unit in environments with multiple components or microservices. |
| Custom metadata version | |
$.metadata.version |
Use custom metadata fields for additional versioning information specific to the organization or project. |
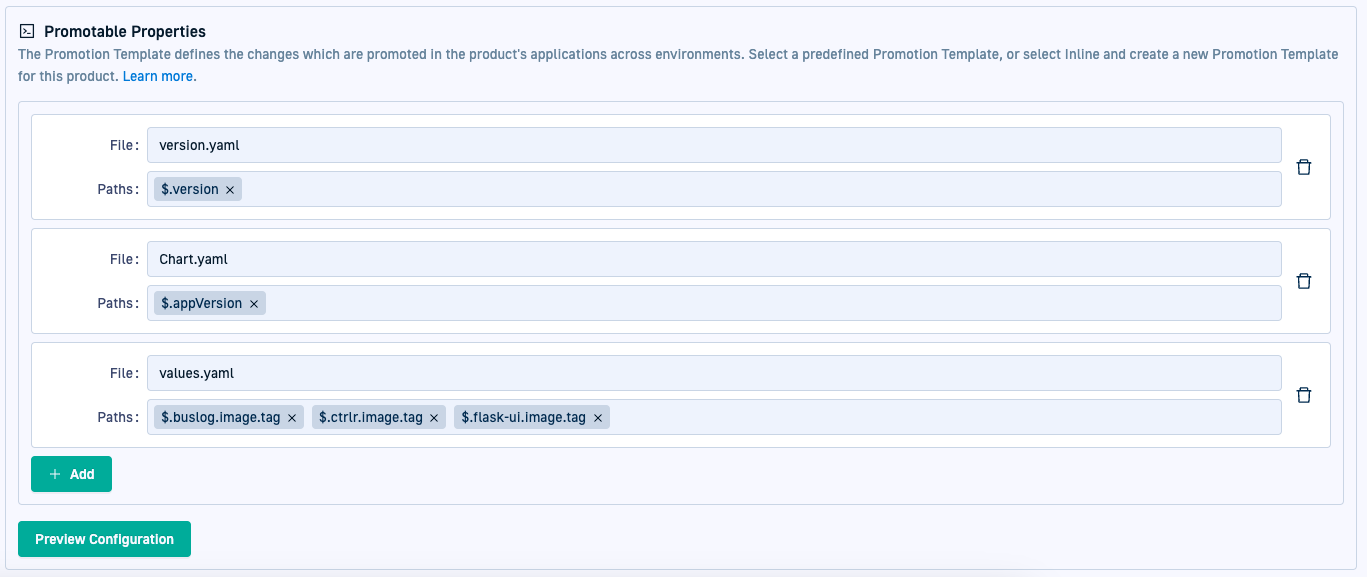
Configuring properties for promotion across applications
Promotable Properties define the files or attributes within files selected for promotion between environments for the applications in a product. Although optional, defining promotable properties allow for precise control over which changes are included in a promotion, ensuring compliance with environment-specific requirements and preventing unwanted modifications.
IMPORTANT
When no Promotable Properties are defined, all files in the application’s source directory are promoted.
This can result in a large data transfer depending on the directory.
Like the Version attribute, Promotable Properties are defined through JSON path expressions. Unlike the Version attribute, you can define multiple JSON path expressions, pointing to different files or to multiple attributes within the same file.
Examples of properties for promotion
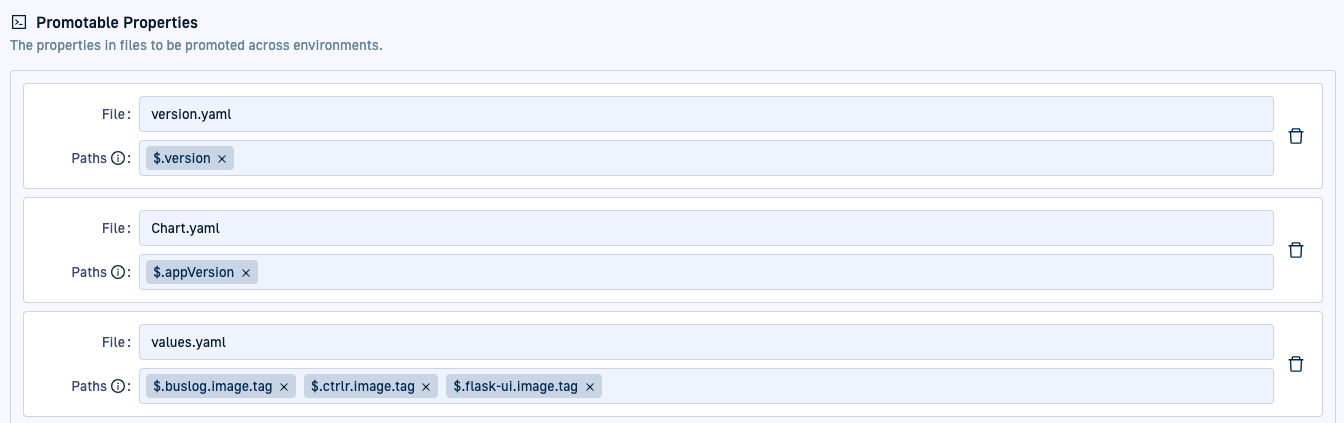
Here’s an example of the Promotable Properties configured for the applications of a Product.
You can see that properties are configured to be promoted from three different files, with values.yaml containing multiple properties to promote.
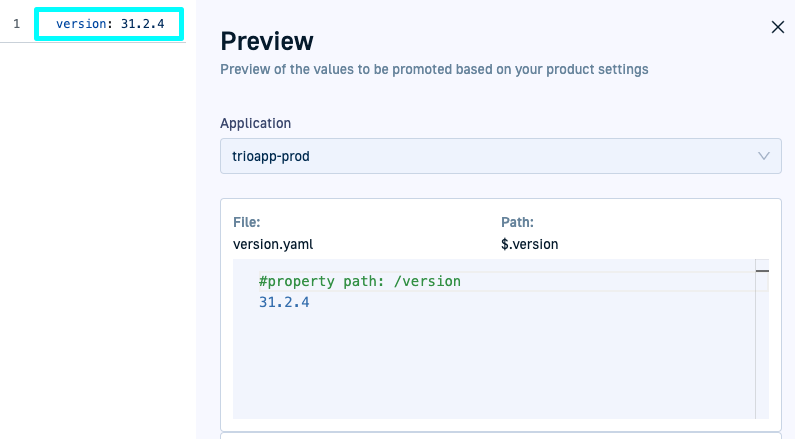
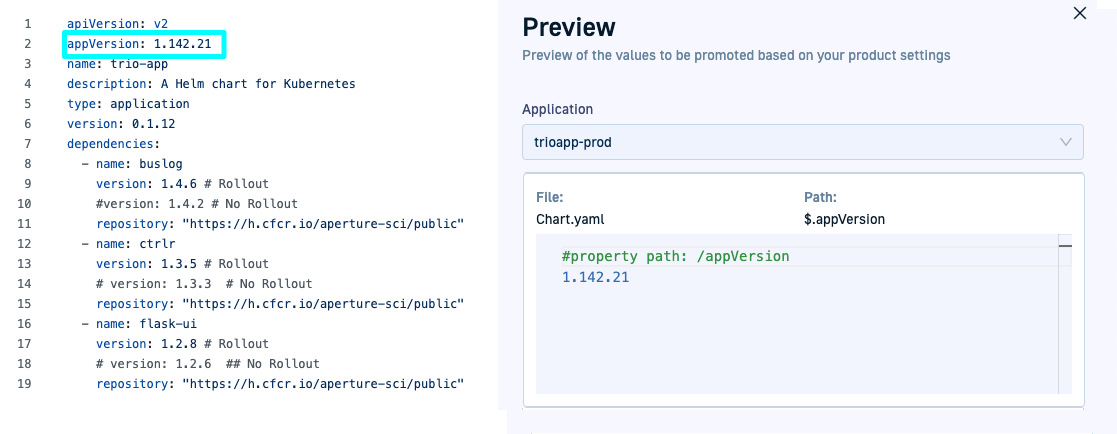
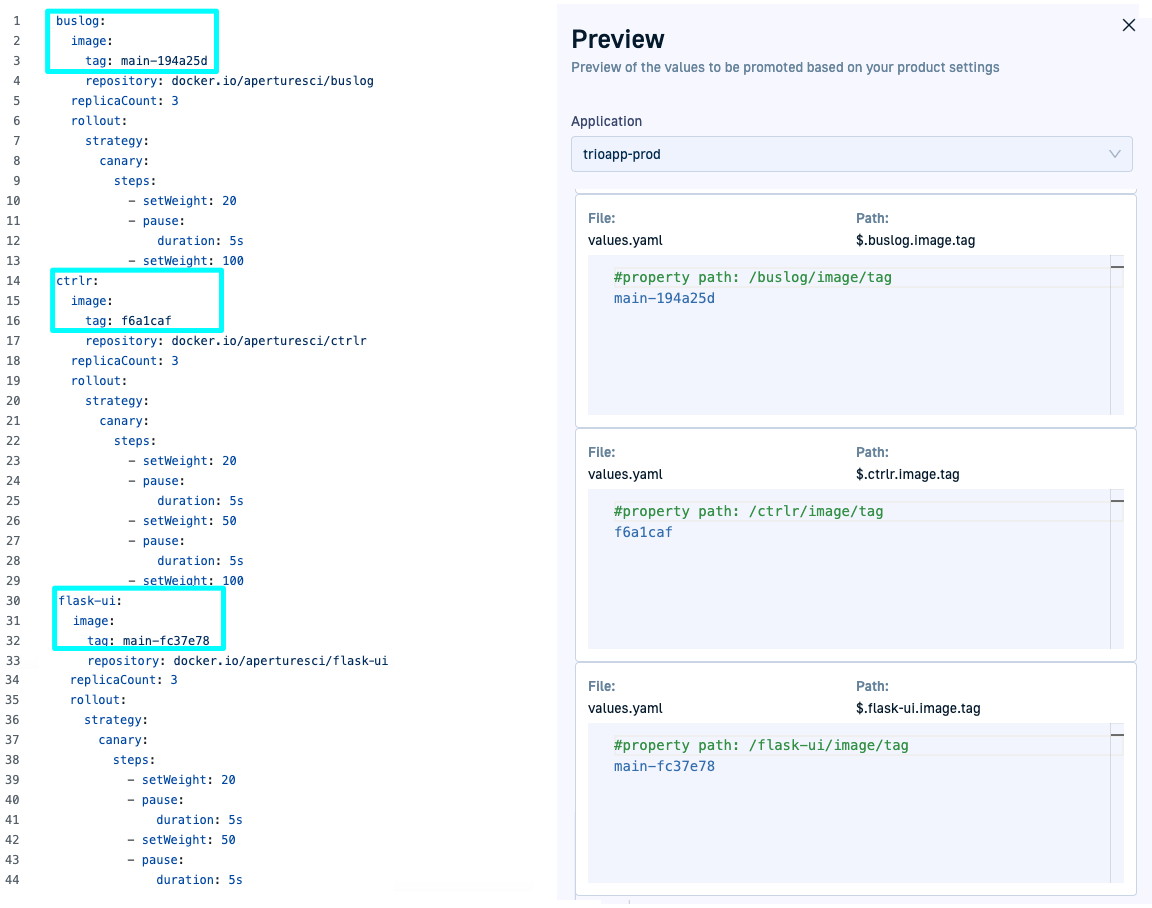
The following examples show how the JSON path expressions are resolved within the different YAML files.
On the left, you can see the YAML manifests, on the right, the previews show how the trio-prod application resolves these values.
`version.yaml’ promoted property resolution & preview
`chart.yaml’ promoted property resolution & preview
`values.yaml’ promoted property resolution & preview
JSON path expressions for files and properties
Application versions and properties to be promoted are defined through JSON path expressions. Each JSON expression points to the specified file and the location of the property within the file.
NOTE
Our promotions are optimized for YAML-based configuration files.
For non-YAML file types, JSON path expressions may not evaluate as expected. In such cases, you can promote the entire file using*as a wildcard.
Autocomplete and path selectors for JSON files
Instead of manually navigating to GitHub, copying the file name, and locating paths within the file, Codefresh GitOps simplifies the process of working with JSON files through auto-selection options:
-
File selector with autocomplete
Typing part of the filename displays a list of available files for selection. -
Path-selector
Clicking the attribute or property directly within the selected file automatically generates and adds the correct JSON path. -
Preview configuration
Verify that the correct property is selected through the Preview Configuration button, which allows you to select the application and view the version retrieved.
You can enter JSON path expressions manually if preferred. See Dashes in JSON keys and JSON syntax for YAML files.
Dashes in JSON keys
Dashes in JSON keys are currently not supported in path expressions using dot notation.
Workaround
Use square bracket notation with double quotes within the brackets to escape the dashes.
For example:
$["rollout-Canary"]["image"]["tag"]
JSON syntax for YAML files
Here’s a brief summary of JSON syntax and rules if you are manually defining path expressions. For detailed information, see JSON syntax.
$
JSON path expressions begin with the $ symbol, which represents the root of the YAML file.
$..
Extracts from all levels of the matching object. Use .. (double dot operator) to navigate and extract from any level within the YAML file.
.*
Extracts all properties. Use .* to retrieve all properties of the matching object.
This is an extract from a sample values.yaml file.
global:
codefresh:
url: g.codefresh.io
tls:
create: false
argo-cd:
tls:
create: true
caCert: 'some-argo-cert'
Using the above syntax:
-
$.global.codefresh.*extracts all attributes that match thecodefreshobject in the file, which resolves to:
url: g.codefresh.ioandtls.create.false -
$..tlsextracts values from all levels withtls, which resolves to:
create: false(fromcodefresh.tlsobject)create: trueandcaCert: some-argo-cert(both fromargo-cd.tlsobject)
Promotion Settings & Promotion Templates
Configure Promotion Settings for the product in either Form or YAML modes.
When you define an Inline template, a new Promotion Template, configure it, and commit the settings, the YAML generated, is saved as a promotion-template resource within the Shared Configuration Repository in the GitOps Runtime selected as the Configuration Runtime.
The path in the Shared Configuration Repo is <gitops-runtime>/<shared-configuration-repo>/resources/configuration/promotion-templates/.
See Shared Configuration Repository and Designating Configuration Runtimes.
To configure directly in YAML, refer to our Promotion Template YAML.
Related articles
Assigning applications to Products
Assigning Promotion Flows and triggers to products
Tracking Product releases
Configure Product Settings