Python Django example
Create Docker images for Python applications
Codefresh can work with Python projects using any of the popular frameworks. In this page we will see Django. For a Flask example see the quick start guide.
The example Django project
You can see the example project at https://github.com/codefreshdemo/cf-example-python-django. The repository contains a Django starter project with the following commands:
pip install -r requirements.txtinstall dependencies.python -m unittest composeexample.utilsruns unit tests.python manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:8000to start the application locally.
Once launched the application presents the Django starter page at localhost:8000.
Django and Docker
The easiest way to build a Django application is with a Dockerfile that contains everything. This is very convenient as the Docker image can contain everything you need (i.e. app plus test frameworks) inside a pipeline.
Here is the Dockerfile:
Dockerfile
FROM python:3.6-slim
ENV PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE 1
ENV PYTHONUNBUFFERED 1
RUN mkdir /code
WORKDIR /code
RUN pip install --upgrade pip
COPY requirements.txt /code/
RUN pip install -r requirements.txt
COPY . /code/
EXPOSE 8000
CMD ["python", "manage.py", "runserver", "0.0.0.0:8000"]This docker build does the following:
- Starts from the Python image
- Sets some environment variables
- Copies the dependencies file inside the container
- Upgrades pip and installs all dependencies
- Copies the rest of the source code
- Starts the Django app
You can build this image locally on your workstation and then launch it to test the application.
Create a CI pipeline for Python/Django
Creating a CI/CD pipeline for Django is very easy if you already have the Dockerfile with all required dependencies.
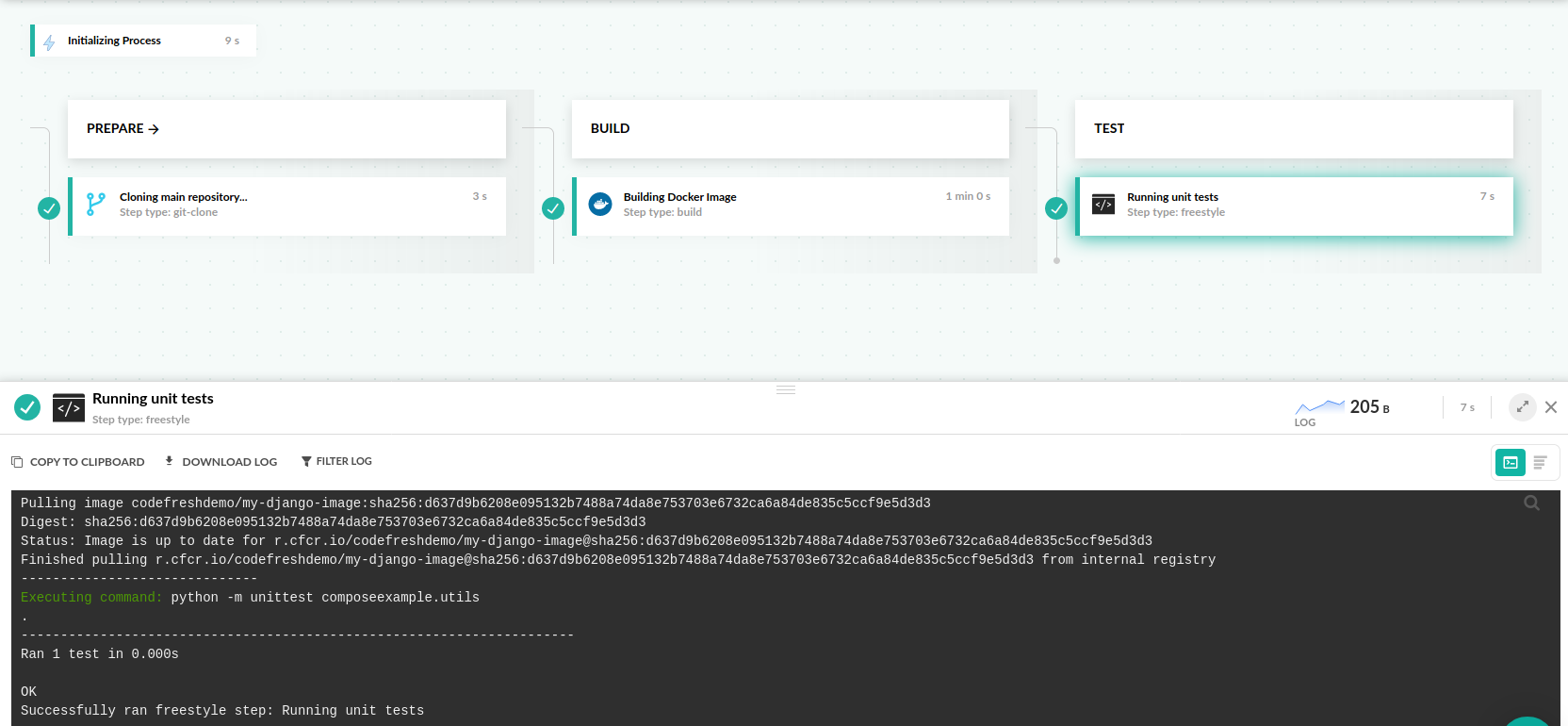
Here is the full pipeline that creates the Docker image after checking out the code.
codefresh.yml
version: '1.0'
stages:
- prepare
- build
- test
steps:
main_clone:
title: Cloning main repository...
stage: prepare
type: git-clone
repo: 'codefreshdemo/cf-example-python-django'
revision: master
git: github
build_my_image:
title: Building Docker Image
stage: build
type: build
image_name: my-django-image
working_directory: ./
tag: master
dockerfile: Dockerfile
test_my_image:
title: Running unit tests
stage: test
image: '${{build_my_image}}'
commands:
- python -m unittest composeexample.utils This pipeline clones the source code, creates a Docker image and then uses the same image to run unit tests. Codefresh is automatically caching Docker layers (it uses the Docker image of a previous build as a cache for the next) and therefore builds will become much faster after the first one finishes.
Running tests before building the docker image
Sometimes if you have a complex application you might want to run integration tests (or other Python commands), before building the Docker image. This scenario is also supported natively by Codefresh.
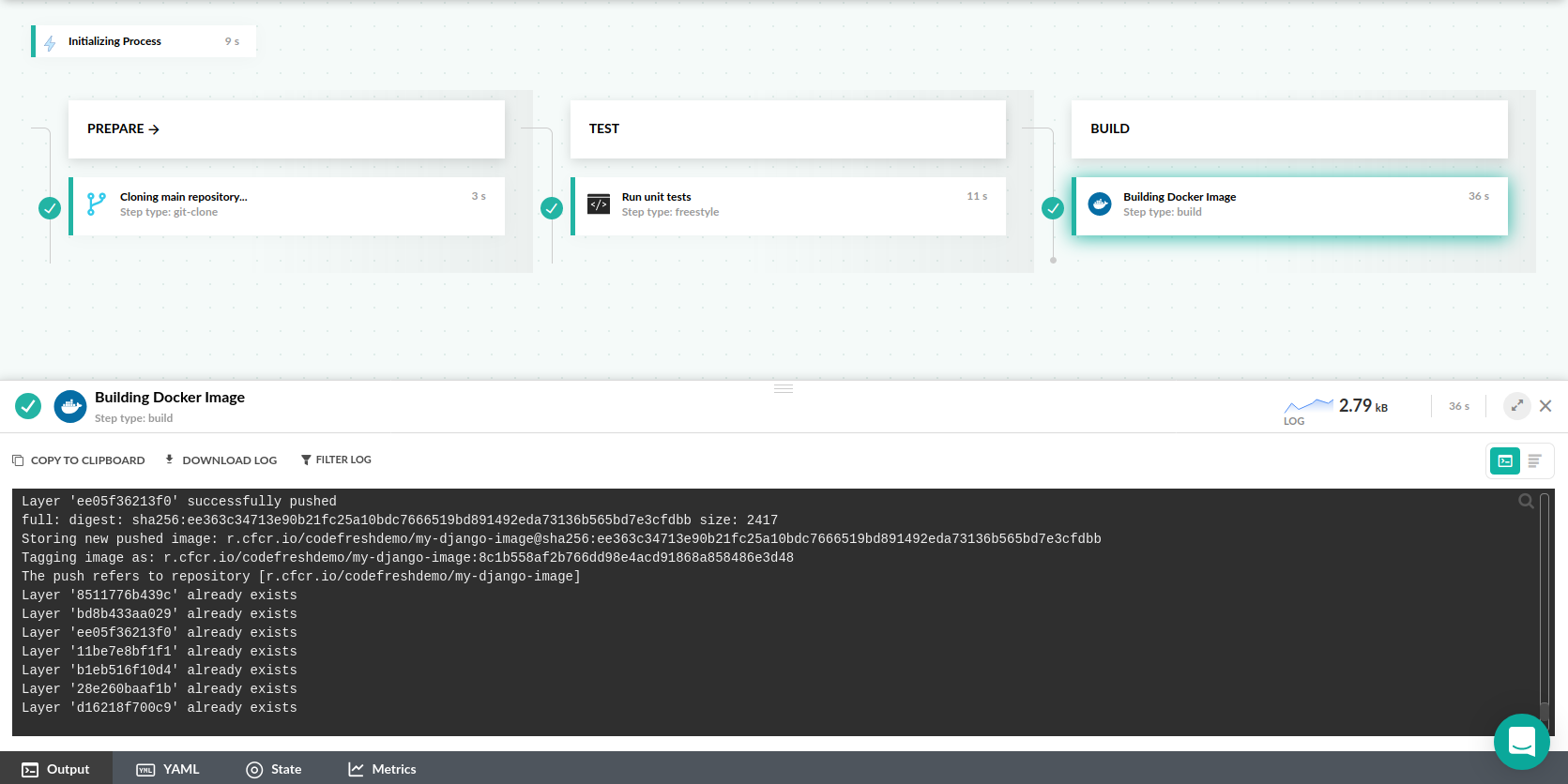
Here is the full pipeline builds the docker image after tests have already executed.
codefresh.yml
version: '1.0'
stages:
- prepare
- test
- build
steps:
main_clone:
title: Cloning main repository...
stage: prepare
type: git-clone
repo: 'codefreshdemo/cf-example-python-django'
revision: master
git: github
test_the_code:
title: Run unit tests
stage: test
image: python:3.6-slim
commands:
- pip install -r requirements.txt --cache-dir=/codefresh/volume/pip-cache
- python -m unittest composeexample.utils
build_my_image:
title: Building Docker Image
stage: build
type: build
image_name: my-django-image
working_directory: ./
tag: full
dockerfile: DockerfileCodefresh is smart enough that caches automatically for us the workspace of a build (/codefresh/volume). This works great for build tools that keep their cache in the project folder, but not for pip which keeps its cache externally (e.g. ~/.cache/pip). By changing the location of the Pip cache on the project folder (the pip-cache name is arbitrary) we make sure that Codefresh will cache automatically the Pip libraries resulting in much faster builds.
Related articles
Python examples
Codefresh YAML for pipeline definitions
Steps in pipelines
Creating pipelines
How Codefresh pipelines work