What Is Argo CD and How Is It Used to Deploy Helm Charts?
Argo CD is a GitOps platform that reads environment configurations and deploys them automatically to a Kubernetes cluster. Kubernetes Helm is a package manager for Kubernetes. A Helm Chart is a YAML configuration, which defines a package of pre-configured resources that can be deployed in a Kubernetes cluster.
Argo CD provides native support for Helm Charts—you can define your applications using a Helm Chart, provide the Helm Charts to Argo CD, and software agents ensure your applications are automatically synchronized and deployed to your CD pipeline. Helm Charts are very useful in a GitOps environment, because they let you define and deploy applications in a declarative manner.
We’ll explain how to apply GitOps to your Helm application and demonstrate how to deploy it to your Kubernetes cluster using Argo CD.
Using Helm Charts with Argo CD and GitOps
GitOps is a set of best practices for declaratively observing and describing a system’s operating infrastructure. You can apply the GitOps methodology throughout the application development workflow, using Git as a single source of truth to actively reconcile and declaratively configure an application. The GitOps paradigm offers transparency between the configurations residing in Git and deployed in clusters.
Argo CD is a GitOps tool that uses this Git-based workflow approach to achieve continuous delivery for Kubernetes. It works as a two-way synchronizing GitOps controller, continuously monitoring running applications, comparing their live state to a desired GitOps configuration, and applying required changes to a cluster. Argo CD also looks for new images in the container registry and updates workload definitions according to your deployment policies.
Related content: Read our guide to Argo with Kubernetes
Argo CD with Helm Charts: How It Works
Before you apply a new or updated Helm chart to a cluster, you must commit it into the repository. Make sure to commit all your YAML workload definitions, Helm charts, and additional resources defining the desired state of a Kubernetes cluster. You can thus ensure a full audit trail of all changes to the cluster and easy rollbacks to any production state in case of issues in your environment.
Argo CD lets you connect your Git repository via HTTPS or SSH, define applications based on Helm charts in your repo, and then automatically synchronize your cluster with the desired state in Git. If your application is OutOfSync, you can resolve this by rolling back or viewing its release history. A successfully synchronized application status will be considered Healthy.
A Healthy application should look like this in the Argo CD user interface:
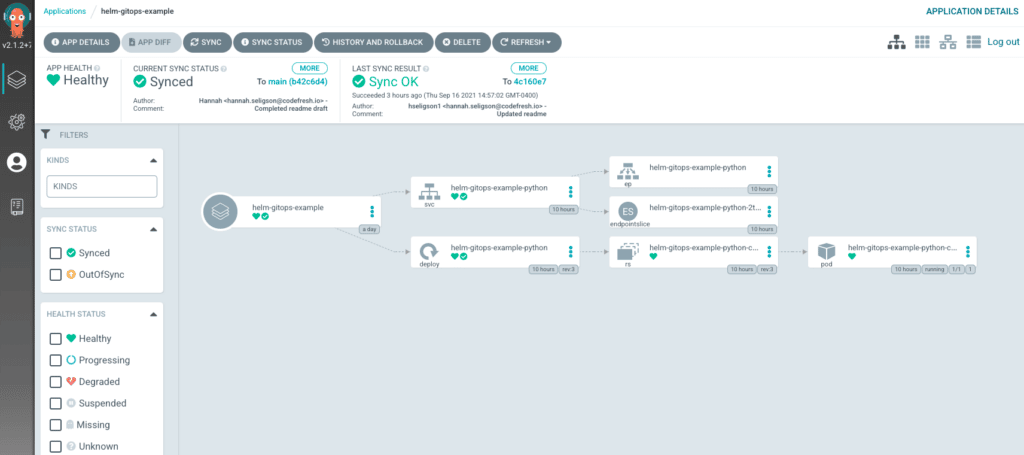
If the application is OutOfSync with your Helm chart, the Helm chart has changed, or its parameters are updated, a new version of the application can be deployed automatically, depending on your deployment strategy.
In case of any issues, you can instantly roll back the deployment using the following command:
argocd app rollback <argocd_app_name> <history_id>
These controls enable complete end-to-end tracking from your Git repository to your Kubernetes cluster and back.
Quick Tutorial: Deploying an Application via Helm Charts in Argo CD
This tutorial will show you how to use the Argo CD UI to set up a Helm repository, create an application based on a Helm chart, and deploy it to a Kubernetes cluster. You can perform the same operations via the CLI. If you want to go beyond the tutorial and prepare a production setup, please read our full guide.
1. Set Up Helm Repositories in Argo CD
Let’s set up a Helm repository in Argo CD so we can access Helm charts.
To set up your Helm repository:
- Start the Argo CD UI.
- Select Settings > Repositories > Connect Repo using… (select the option relevant for your repo—SSH, HTTPS, or GitHub App).
- Set Type to Helm and specify a unique Name and Repository URL for your repository. If it is a private repository, add access credentials.
2. Create an Application in Argo CD Defined By a Helm Chart
Now, we’ll create an application entity within Argo CD, and define application structure and configuration by providing a Helm chart.
To set up an application via Helm chart:
- In the Argo CD UI, select Applications and click New App.
- Fill in a unique Application Name, a Project used to group applications together, and a Sync Policy—for simplicity, leave this as Manual.
- Under Repository URL, select the repo you defined earlier.
- The Chart field now populates with Helm charts available in your repository. Select a Helm chart.
- The Revision field populates with revisions of the Helm chart you selected—choose the revision you want to deploy.
- Fill in the details of the destination Kubernetes cluster in which you want to deploy your application—Cluster URL and Namespace (the namespace must already exist in the cluster, or you can auto-create a new namespace).
- Click Create—Argo CD confirms the parameters and shows the application, initially with status OutOfSync, because it is not yet deployed to the cluster.
3. Deploy the Application
To deploy the application via the Helm chart you selected:
- Select the application tile in the dashboard.
- Select synchronization options—for now, leave them as default, which will synchronize all manifests. To understand advanced options like Pruning and Dry Run, see the documentation.
- Click the Synchronize button. Argo CD deploys the application to the Kubernetes cluster.
- The dashboard now shows the application, as defined in the Helm chart, running on pods in your Kubernetes cluster. You can also run
kubectl get allto see the pods created from the Helm chart.
Important note: When you deploy Helm charts with Argo CD they are no longer recognized as Helm deployments by Kubernetes. Regular Helm commands may not work, because the application is considered by Kubernetes as an Argo CD application, not a Helm deployment.
4. Using Values Files with Helm in Argo CD
Helm allows the use of different or multiple values.yaml files for parameter configuration. These can be specified in Argo CD using the –values flag or declarative syntax.
Here is how to deploy a Helm file with Argo CD while setting values, via the command line:
argocd app set helm-guestbook --values values-production.yaml
And here is how to specify values directly in the Application manifest:
source:
helm:
valuesObject:
ingress:
enabled: true
path: /
hosts:
- mydomain.example.com
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
kubernetes.io/tls-acme: "true"
labels: {}
tls:
- secretName: mydomain-tls
hosts:
- mydomain.example.com
Another way is to pass values as a string:
source:
helm:
values: |
ingress:
enabled: true
path: /
hosts:
- mydomain.example.com
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
kubernetes.io/tls-acme: "true"
labels: {}
tls:
- secretName: mydomain-tls
hosts:
- mydomain.example.com
5. Overriding Values with Parameters
Helm parameters override values in values.yaml files. These can be set in Argo CD via command line or declarative syntax.
Here is how to do it via the command line:
argocd app set helm-guestbook -p service.type=LoadBalancer
Here is how to do it declaratively via the application manifest:
source:
helm:
parameters:
- name: "service.type"
value: LoadBalancer
Note that values are injected in the following order of precedence:
- Parameters (parameters)
- Values Object (valuesObject)
- Values (values)
- Value Files (valueFiles)
Learn More About GitOps and Helm Chart Deployment
Helm can be very helpful as a familiar component that can help teams transition from traditional workflows to GitOps. Here are additional articles that can help you use Helm charts with GitOps:
- Using Helm with GitOps – explores Helm, shows how Helm charts are mapped to Kubernetes manifests, and provides practical guidance for using Helm with GitOps.
- How to Simplify Your Kubernetes Helm Deployments – explains what to do if the Helm chart promotion process becomes complicated and difficult to automate. Learn a few Helm techniques that can make your process simpler and more robust.
- Using Help to Deploy a Kubernetes Application to Multiple Environments – shows how to use Helm to address a common deployment challenge – how to handle QA, staging, and production environments during the software lifecycle.
- Unlimited Preview Environments with Kubernetes Namespaces – shows how to create testing environments on demand for each pull request.
The World’s Most Modern CI/CD Platform
A next generation CI/CD platform designed for cloud-native applications, offering dynamic builds, progressive delivery, and much more.
Check It Out