Microservices is an architectural pattern where an application is built as a collection of small, loosely coupled, and independently deployable services. Each microservice is responsible for a specific functionality or domain, and they communicate with each other using APIs. This architectural pattern promotes flexibility, scalability, and maintainability, as changes can be made to a single microservice without affecting the entire application.
AWS is a leading cloud platform that provides a wide range of services for developers to build, deploy, and run applications. When it comes to microservices, AWS offers various tools and services that can help developers design, implement, and manage microservices-based applications. With its global infrastructure, high availability, and pay-as-you-go pricing model, AWS is an excellent environment for deploying and scaling microservices applications.
There are several advantages to building microservices in AWS, including:
- Scalability: Microservices can be scaled independently, allowing you to allocate resources to specific services based on their requirements. AWS provides various services, like Elastic Container Service (ECS) and Lambda, that enable you to scale your microservices easily and efficiently.
- Flexibility: With microservices, you can use different programming languages, frameworks, and databases for each service. This allows you to choose the best technology stack for each microservice, optimizing performance and resource utilization.
- Resiliency: By breaking down your application into small, isolated services, you can improve its resilience. If one microservice fails, it doesn’t necessarily mean that the entire application will fail. AWS provides tools for monitoring and recovering from failures, ensuring that your application remains highly available.
- Faster deployment: Each microservice is independent, so you can deploy updates and new features without affecting the entire application. This enables faster and more frequent releases, accelerating your development cycle.
Learn more in our detailed guide to microservices architecture
Why Do Organizations Use the Microservices Pattern in AWS?
Building Cloud-Native Applications
Microservices play a crucial role in building cloud-native applications on AWS. Cloud-native applications are designed to take full advantage of the cloud environment, leveraging its scalability, elasticity, and distributed nature. By breaking your application into smaller, self-contained services, you can build a highly scalable and resilient system that can adapt to changing business requirements and customer demands.
Enhancing DevOps Practices
Microservices can also help enhance DevOps practices on AWS. DevOps is a culture that promotes collaboration between development and operations teams to deliver high-quality software quickly and reliably. With microservices, development teams can work on different services in parallel, reducing the risk of conflicts and bottlenecks.
Additionally, deploying and managing microservices on AWS using infrastructure-as-code (IAC) tools like AWS CloudFormation can help automate your infrastructure provisioning and management, further improving your DevOps processes.
Supporting Digital Transformation
Many organizations are undergoing digital transformation to stay competitive in today’s fast-paced business environment. Embracing microservices on AWS can help accelerate this transformation by enabling you to build agile, scalable, and resilient applications that can quickly adapt to new business opportunities and challenges.
Learn more in our detailed guide to microservices best practices (coming soon)
AWS Services for Microservices
AWS provides several cloud services that are uniquely suited to a microservices architecture. You can use these services to quickly set up microservices applications in the cloud.
Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS)
ECS is a fully managed container orchestration service that allows you to deploy, manage, and scale Docker containers on AWS. It is considered a simpler alternative to Kubernetes. It provides deep integration with other AWS services, such as Elastic Load Balancing, Amazon RDS, and AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM). ECS is an excellent choice for deploying microservices on AWS, as it enables you to easily scale your services and manage their lifecycle.
AWS Lambda
AWS Lambda is a serverless compute service that lets you run your code without provisioning or managing servers. With Lambda, you can build serverless microservices that automatically scale with the number of requests, without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. Lambda supports various programming languages, such as Python, Node.js, and Java, allowing you to build microservices using your preferred language.
Amazon API Gateway
API Gateway is a fully managed service that makes it easy to create, publish, and manage APIs for your microservices. It provides features like caching, logging, security, and monitoring, enabling you to build robust and scalable APIs for your microservices. By using API Gateway, you can also create custom domain names and generate client SDKs to simplify the integration of your microservices with other applications.
AWS Step Functions
Step Functions is a serverless workflow service that helps you coordinate your microservices and build complex applications. It allows you to define and execute state machines that orchestrate multiple AWS Lambda functions and other AWS services. By using Step Functions, you can simplify the coordination and error handling of your microservices, improving their reliability and maintainability.
Amazon Reference Architecture for Microservices
The diagram below shows a reference architecture for an AWS-based microservices application. Let’s review the key components of this architecture (discussion is based on the Amazon documentation).
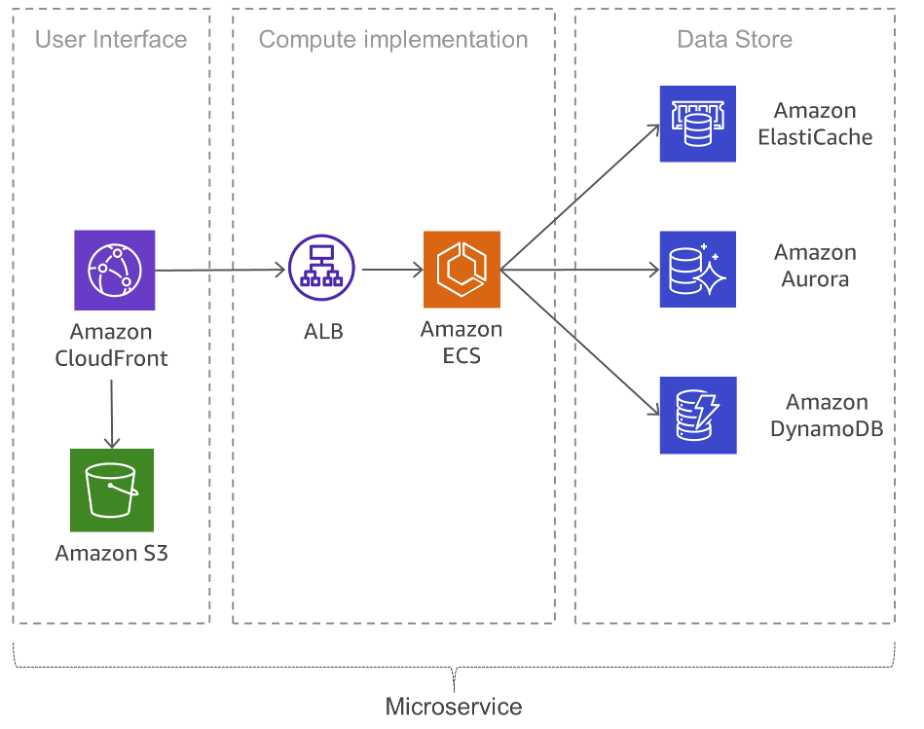
User Interface
Contemporary web applications predominantly use JavaScript frameworks to create single-page applications that communicate via REST or RESTful API. Amazon’s Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) and Amazon CloudFront can manage static web content. Since a microservice’s clients receive service from the nearest edge location and fetch responses from a cache or a proxy server with optimized connections to the source, latency is considerably reduced.
Microservices
AWS provides several integrated components that support the deployment of microservices, either as serverless functions or containers:
- AWS Lambda allows you to upload your code, after which Lambda manages everything required to run and scale your implementation to meet your actual demand curve—without any need for infrastructure management. Lambda supports many programming languages and can be invoked directly from any web or mobile app or from other AWS services.
- AWS Fargate is a serverless computing engine that facilitates containers, working with both Amazon ECS and Amazon EKS. It takes care of provisioning adequate compute resources for running your container applications.
- Amazon ECS lets you customize how it places and ends tasks through container placement strategies and constraints. A task placement constraint is a rule considered during task placement. You can assign attributes to your container instances and use a constraint to place tasks based on these attributes.
- Amazon EKS manages Kubernetes and keeps it updated, while allowing you to make use of existing plugins and tooling from the Kubernetes community. Applications on Amazon EKS are fully compatible with those running on any standard Kubernetes environment, whether it’s in an on-premises data center or public clouds.
- Amazon ECR lets you store Docker images used in Amazon ECS or Amazon EKS in a managed container registry. Amazon ECR reduces the need to manage and scale the infrastructure necessary for your container registry.
Data Store
A data store is used to preserve microservice data. Commonly used stores for session data are in-memory caches like Memcached or Redis. Amazon provides both technologies as part of the managed Amazon ElastiCache service.
If the microservices app needs relational databases, AWS offers six database engines as managed services through Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS). Another option is NoSQL databases, which emphasize scalability, performance, and availability. Amazon DynamoDB allows you to create database tables that can store any amount of data and cater to any level of traffic.
Best Practices for Implementing Microservices on AWS
Leverage Amazon Automation Capabilities
Automate your infrastructure provisioning, deployment, and management using tools like AWS CloudFormation. By automating these processes, you can reduce human errors, improve consistency, and accelerate your development and deployment cycles.
Implement Robust Monitoring and Logging
Monitoring and logging are essential for maintaining the health and performance of your microservices. Use AWS services like Amazon CloudWatch, AWS X-Ray, and AWS CloudTrail to collect metrics, traces, and logs. This data can help you identify and resolve issues, optimize resource usage, and improve the overall performance of your microservices.
Secure Your Microservices
Security should be a top priority when building microservices on AWS. Use AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) to control access to your microservices and AWS resources. Also, implement encryption, both in transit and at rest, to protect your data. Finally, use tools like AWS WAF and AWS Shield to protect your microservices from security threats.
Plan for Failure
Design your microservices for resiliency by planning for failure. Implement strategies like circuit breakers, retries, and fallbacks to handle failures gracefully. Additionally, use AWS services like Auto Scaling and Amazon Route 53 to ensure high availability and fault tolerance for your microservices.
By following these best practices and leveraging the powerful tools and services provided by AWS, you can master microservices and build scalable and high-performing applications. Start your journey today and take your application development to the next level.
Make an Informed Choice Between Serverless, Containers, and Full Kubernetes
When choosing your runtime platform, consider the following:
- AWS Lambda is best for lightweight microservices with unpredictable demand or quick, stateless tasks, allowing developers to focus on their code without concerning themselves with the underlying infrastructure.
- Amazon ECS is suitable for long-running applications and microservices that need some orchestration, but do not need the full power of Kubernetes.
Amazon EKS is suitable for organizations that have adopted Kubernetes as their orchestration standard, offering extensive customization and control but demanding more resources and expertise for management.
Microservices with Codefresh
Codefresh is designed with building and delivering microservices in mind providing end-to-end support that significantly reduces the additional complexity. Codefresh pipelines provide flexible triggers that make adding new microservices to existing pipelines easy, ensuring that your CI pipelines stay DRY. With the advanced caching capabilities, similar microservices will have dramatically reduced build times.
Codefresh also helps you answer critical questions within your organization, whether you’re a developer, or a product manager:
- What features are deployed right now in any of your environments?
- What features are waiting in Staging?
- What features were deployed on a certain day or during a certain period?
- Where is a specific feature or version in our environment chain?
With Codefresh, you can answer all of these questions by viewing one dashboard, our Applications Dashboard that can help you visualize an entire microservices application in one glance:
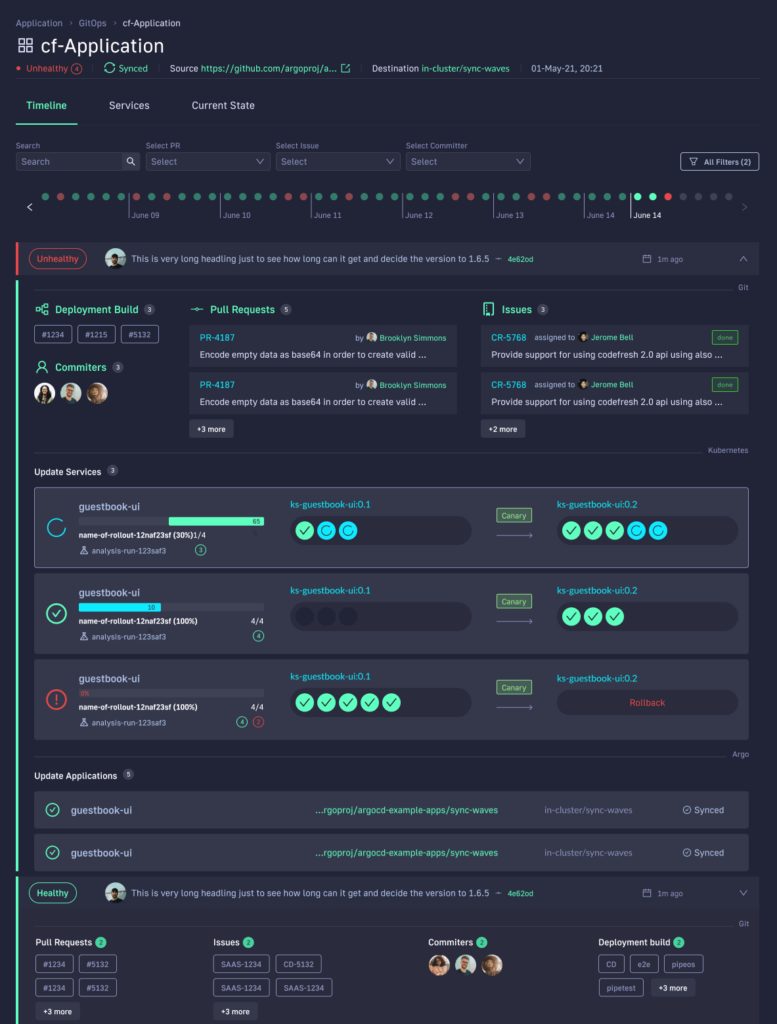
The World’s Most Modern CI/CD Platform
A next generation CI/CD platform designed for cloud-native applications, offering dynamic builds, progressive delivery, and much more.
Check It Out