Argo CD has built a number of Generators to support various scenarios that developers need when using Argo CD and Kubernetes. In this post, I’ll be discussing the Pull Request Generator. A Pull Request Generator is an Argo CD Application Set deployment type that is configured to “watch” a Git repository for Pull Requests (PRs). Whenever a new PR is submitted that matches the specified filter, Argo CD applies the manifests from the referenced repository and path. This allows you to test the PR changes in an ephemeral environment. In addition, the Pull Request Generator cleans up after itself when the PR is closed, removing the resources that it deployed.
The manifest for a Pull Request Generator can look quite daunting as there is some additional configuration required to make it work. In this post, I’ll break down the manifest so it is a little more consumable.
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: ApplicationSet
metadata:
name: octopub-pullrequestgenerator
namespace: argocd
spec:
goTemplate: true
goTemplateOptions: ["missingkey=error"]
generators:
- pullRequest:
requeueAfterSeconds: 120
bitbucketServer:
project: pul
repo: pullrequestgenerator
# URL of the Bitbucket Server. Required.
api: https://bitbucket.octopusdemos.app
# Credentials for Basic authentication (App Password). Either basicAuth or bearerToken
# authentication is required to access private repositories
# Credentials for Bearer Token (App Token) authentication. Either basicAuth or bearerToken
bearerToken:
# Reference to a Secret containing the bearer token.
tokenRef:
secretName: bitbucket-token
key: token
# authentication is required to access private repositories
# Labels are not supported by Bitbucket Server, so filtering by label is not possible.
# Filter PRs using the source branch name. (optional)
filters:
- branchMatch: ".*-argocd"
template:
metadata:
name: 'octopub-{{.branch}}-{{.number}}'
spec:
source:
repoURL: 'https://bitbucket.octopusdemos.app/scm/pul/pullrequestgenerator.git'
targetRevision: '{{.head_sha}}'
path: manifests
project: "default"
destination:
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
namespace: 'octopub-{{.branch}}-{{.number}}'
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
selfHeal: true
syncOptions:
- Validate=false
- CreateNamespace=true
Kind
To support multiple PRs existing at the same time, the Pull Request Generator must use an ApplicationSet. An ApplicationSet acts as an “application factory” to automatically generate applications from a single manifest file.
kind: ApplicationSet
Spec: Generators
Within the manifest specification (spec), you can define one or more generators. This post focuses on the Pull Request Generator specifically, which is denoted by pullRequest.
spec: goTemplate: true goTemplateOptions: ["missingkey=error"] generators: - pullRequest:
By default, Argo CD will check for pull requests every 30 minutes. The manifest provides a method to override this value called requeueAfterSeconds. In my example, I’ve configured Argo CD to check for PRs every two minutes (120 seconds)
Note: Exercise caution when configuring the requeueAfterSeconds as it could lead to API rate limitation for cloud-based source control managers.
- pullRequest:
requeueAfterSeconds: 120
Repo Server
Git providers implement the Git API in the same way for most commands such as pulling, pushing, fetching, etc., except for Pull Request. This requires that the Pull Request Generator specify which Git repository it is using so that it makes the appropriate API calls. In my example, I configured the Pull Request Generator to work with my Bitbucket Server instance (see here for a list of Git repository providers and the specifics for configuring them).
- pullRequest:
requeueAfterSeconds: 120
bitbucketServer
For the Bitbucket Server configuration, you’ll need to define the following:
- Project
- Repo
- Api
- Authentication
Project
The Argo CD example in their documentation is misleading when it comes to this value. Their example makes it look like this is the Bitbucket Project name; however, it is the Project key value it is looking for. (Bitbucket Server capitalizes the Project key, however, manifests require these values to be lower-case).
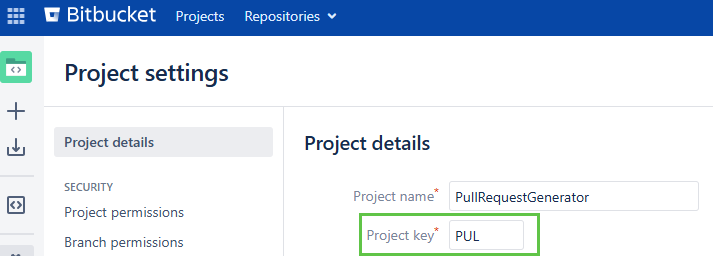
- pullRequest:
requeueAfterSeconds: 120
bitbucketServer:
project: pul
Repo
Projects within Bitbucker Server may have multiple repositories configured. This is the name of the repository you would like Argo CD to monitor.
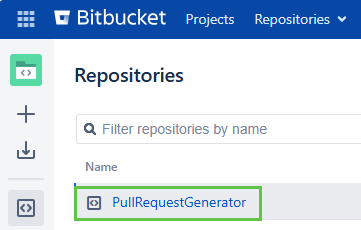
- pullRequest:
requeueAfterSeconds: 120
bitbucketServer:
project: pul
repo: pullrequestgenerator
API
This value is simply the URL to the Bitbucket Server instance. In my case, it is https://bitbucket.octopusdemos.app
- pullRequest:
requeueAfterSeconds: 120
bitbucketServer:
project: pul
repo: pullrequestgenerator
# URL of the Bitbucket Server. Required.
api: https://bitbucket.octopusdemos.app
Authentication
Argo CD needs to be able to authenticate to the Bitbucket Server so it can monitor the requested repositories. The Bitbucket Server implementation offers two authentication mechanisms:
- BasicAuth
- BearerToken
My example uses the BearerToken method. This value is a Personal Access Token (PAT) for Bitbucket Server
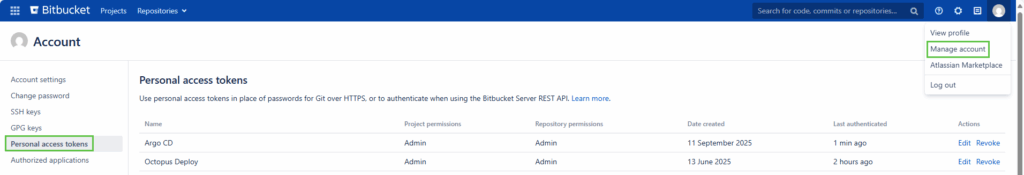
Argo CD uses Kubernetes resources for this authentication, so the PAT is stored as a Secret within your cluster. This can be created using something similar to this:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: bitbucket-token
labels:
argocd.argoproj.io/secret-type: repository
namespace: argocd
type: Opaque
stringData:
token: <Personal Access Token value>
This secret is then referred to in the bearerToken section
- pullRequest:
requeueAfterSeconds: 120
bitbucketServer:
project: pul
repo: pullrequestgenerator
# URL of the Bitbucket Server. Required.
api: https://bitbucket.octopusdemos.app
# Credentials for Bearer Token (App Token) authentication. Either basicAuth or bearerToken
bearerToken:
# Reference to a Secret containing the bearer token.
tokenRef:
secretName: bitbucket-token
key: token
Filters
Filters are how you tell the Pull Request Generator what to match on. In my example, I’m telling Argo CD to create resources only when a PR is created in branches that end in “-argocd”. The match is done with a regular expression so the period is required, despite not being in the branch name.
- pullRequest:
requeueAfterSeconds: 120
bitbucketServer:
project: pul
repo: pullrequestgenerator
# URL of the Bitbucket Server. Required.
api: https://bitbucket.octopusdemos.app
# Credentials for Bearer Token (App Token) authentication. Either basicAuth or bearerToken
bearerToken:
# Reference to a Secret containing the bearer token.
tokenRef:
secretName: bitbucket-token
key: token
# authentication is required to access private repositories
# Labels are not supported by Bitbucket Server, so filtering by label is not possible.
# Filter PRs using the source branch name. (optional)
filters:
- branchMatch: ".*-argocd"
Template
This section defines the template to use when creating the Kubernetes resources. For the Pull Request Generator, we can utilize some variables such as the branch name ( {{.branch}} ) and the numerical value of the PR ( {{.number}} )
template:
metadata:
name: 'octopub-{{.branch}}-{{.number}}'
Spec
The Spec section of a Template follows the same pattern as the standard ApplicationSet specification. The biggest difference is going to be in the targetRevision and namespace sections. You are able make use of the variables previously mentioned to create unique namespaces so that each PR has its own, ephemeral environment. The targetRevision needs to match the PR, this is one of the few times where you can deviate from the recommended GitOps principal of using something other than HEAD.
spec:
source:
repoURL: 'https://bitbucket.octopusdemos.app/scm/pul/pullrequestgenerator.git'
targetRevision: '{{.head_sha}}'
path: manifests
project: "default"
destination:
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
namespace: 'octopub-{{.branch}}-{{.number}}'
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
selfHeal: true
syncOptions:
- Validate=false
- CreateNamespace=true
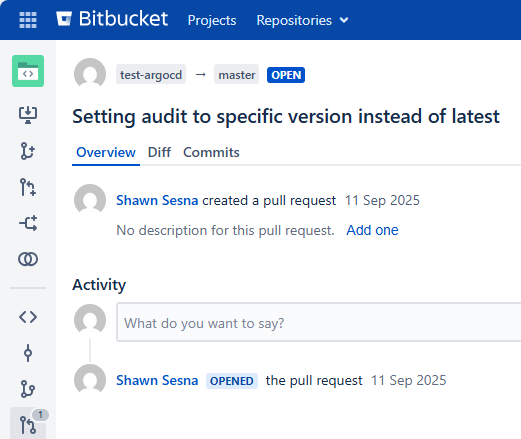
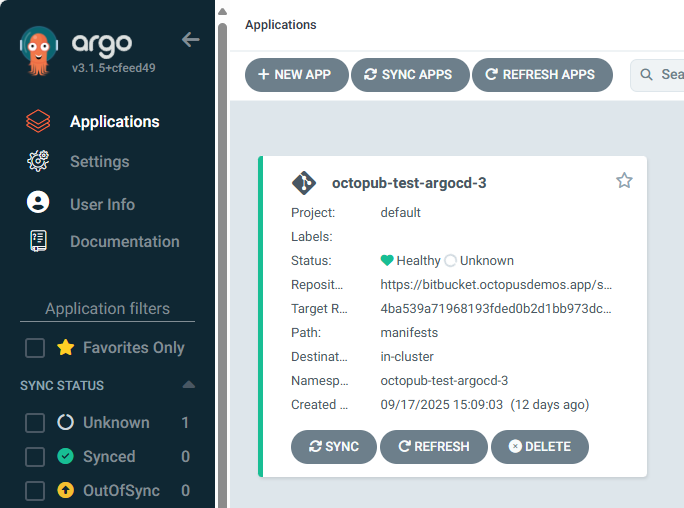
Seeing it in action
If everything is configured correctly, whenever a new PR with the specified filter is created, you will see a new application created within Argo CD!
Conclusion
The Pull Request Generator is a powerful tool that can help reduce bugs by providing a mechanism of testing PRs before they are merged. In this post, I broke down the Pull Request Generator to help understand what it does and how to construct one.
