Install GitOps Runtime with new Argo CD
Provision GitOps Runtimes with a new Argo CD installation through Helm
GitOps Runtime with new Argo CD
This article describes how to install the GitOps Runtime in a Codefresh accounts using a Helm chart on a cluster without an Argo CD instance.
Runtime values.yaml
The Codefresh values.yaml located here, contains all the arguments you can configure, including optional ones.
Review how Codefresh validates the Runtime’s values.yaml.
To install the GitOps Runtime with an existing Argo CD instance, see Install GitOps Runtime with existing Argo CD.
Before you begin
- Make sure you meet the minimum requirements for installation
- Verify that you complete all the prerequisites
Step 1: Select Runtime install option
- On the Getting Started page, click Install Runtime.
Step 2: Set up GitOps Git provider
As a one-time action, define the Shared Configuration Repository and associate it with your Git provider.
The Git provider you select for the first GitOps Runtime applies to all Runtimes in the same account.
Shared Configuration Repository
The Shared Configuration Repository is a Git repository which stores configuration manifests shared between all the GitOps Runtimes within the same account. Codefresh identifies the Git provider from the URL of the Shared Configuration Repo, and for cloud providers, automatically populates the Git Provider and the API URL fields.
NOTE:
The Shared Configuration Repository and Git provider are configured once per account and are not required for additional Runtimes within the same account.
You can specify only the repository URL, or add the path, reference a branch, or both:
<repo_url>.git[/<path>][?ref=<branch>]
where:
-
<repo_url>.gitis required and is the repository URL. This is the standard URL format which references the root of the default branch in the repository. The.gitsuffix is recommended. Example:https://github.com/codefresh-io/our-isc.git -
<path>is optional, and points to a specific path within the repository.
Use<path>if you want your configuration files within a subdirectory.
Example:https://github.com/codefresh-io/our-isc.git/some/path -
<branch>is optional, and references a specific branch in the repository.
Example:https://github.com/codefresh-io/our-isc.git?ref=isc-branch
Step 3: Install GitOps Runtime
To install the GitOps Runtime, follow the instructions in the installation wizard which provides an Install Runtime command with pre-populated values.
Runtime Name
By default, the runtime name is codefresh.
If you define a custom name, it must:
- Start with a lowercase letter
- Contain only lowercase letters and numbers
- Be no longer than 38 characters
NOTE
If you are installing an additional Runtime in the same account, the Runtime name must be unique.
Namespace
The namespace where install the GitOps Runtime is installed, and must conform to Kubernetes naming conventions.
Codefresh API Key
The API key authenticates the GitOps Runtime with the Codefresh platform, enabling secure registration, configuration retrieval, and communication with Codefresh services.
Generate the API key to automatically include it in the Runtime Install command.
Install Runtime command
The Install Runtime Command differs based on the access mode. The command below is for the tunnel-based access mode. This is the default access mode and does not require any additional flags.
Ingress-based or service-mesh-based access modes require additional flags, as described in GitOps Runtimes with ingress controllers/service meshes.
Tunnel-based install chart command
helm upgrade --install <helm-release-name> \
--create-namespace \
--namespace <namespace> \
--set global.codefresh.accountId=<codefresh-account-id> \
--set global.codefresh.userToken.token=<codefresh-api-key> \
--set global.runtime.name=<runtime-name> \
oci://quay.io/codefresh/gitops-runtime \
--waitInstall command parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
<helm-release-name> |
Name of the Helm release. The default is cf-gitops-runtime, which you can change if needed. |
<namespace> |
Namespace where the GitOps Runtime is installed. Default is codefresh, or a custom name you define. |
<codefresh-account-id> |
Mandatory only for tunnel-based Runtimes (default access mode). Automatically populated by Codefresh. |
<codefresh-api-key> |
API key used for authentication. You can use an existing key or generate a new one. Automatically populated in the command when generated. |
<runtime-name> |
Name of the GitOps Runtime. Default is codefresh, or a custom name you define. |
gitops-runtime |
Chart name defined by Codefresh. Cannot be changed. |
--wait |
Optional. The duration the installation process waits for all pods to become ready before timing out. Recommend to set it to a period longer than 5 minutes which is the default if not set. |
Step 4: Completing Installation
After installation, you can:
- Continue with the Configuration & Management steps in the installation wizard. See Configure GitOps Runtime.
- View the installed Runtime in the Runtimes page.
- Depending on your setup, complete the post-installation configuration:
- For private registries, you need to override specific image values.
- If your Git servers are on-premises, add custom repository certificates.
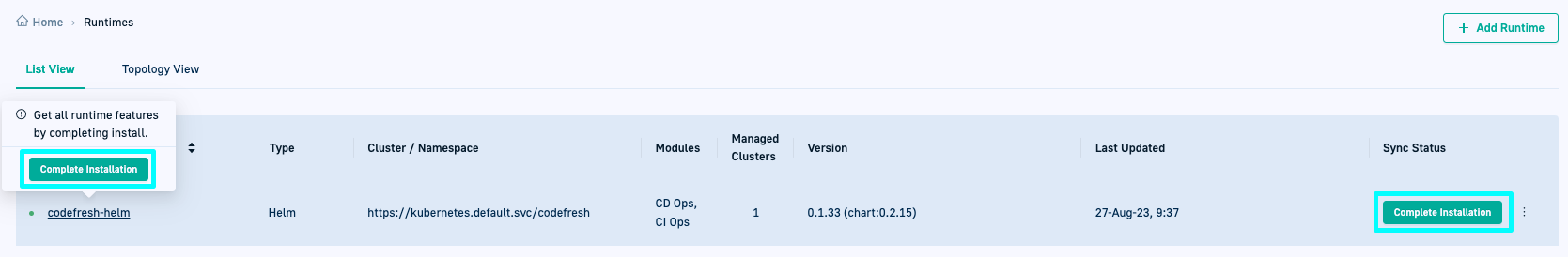
View installed Runtime
After installation, go to GitOps Runtimes > List View:
- A green dot indicates the Runtime is online.
- The Type column shows Helm with the label Config Runtime, indicating it has been designated as the Configuration Runtime.
- The Sync Status column displays either:
- Synced: Configuration is complete
- Complete Installation: Pending configuration steps
- Drill down into the Runtime shows tabs for Runtime Components, Git Sources, and Managed Clusters.
The Runtime Components are populated only when the GitOps Runtime is configured as an Argo CD Application, as described here.
Optional GitOps Runtime configuration
Image overrides for private registries
If you use private registries, you must override specific image values for the different subcharts and container images.
Our utility helps override image values for GitOps Runtimes by creating values files that match the structure of the subcharts, allowing you to easily replace image registries. During chart installation, you can provide these values files to override the images, as needed.
For more details, see ArtifactHub.
Custom repository certificates
Repository certificates are required to authenticate users to on-premises Git servers.
If your Git servers are on-premises, add the repository certificates to your Codefresh values file, in .values.argo-cd. These values are used by the Argo CD that Codefresh deploys. For details on adding repository certificates, see this section.
global:
codefresh:
tls:
caCerts:
# optional - use an existing secret that contains the cert
# secretKeyRef:
# name: my-certificate-secret
# key: ca-bundle.crt
# or create "codefresh-tls-certs" secret
secret:
create: true
content: |
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
...
-----END CERTIFICATE-----Install GitOps Runtime via Terraform
You can also use Terraform to install an additional GitOps Runtime with the Helm provider.
NOTE
Every Runtime in an account must have a unique name. If you usedcodefresh(the default) for the first Runtime, choose a different name to avoid installation failures.
Here is an example:
resource "helm_release" "my_gitops_runtime" {
name = "my-codefresh-runtime"
repository = "oci://quay.io/codefresh"
chart = "gitops-runtime"
namespace = "my-codefresh-runtime"
version = "0.2.14"
create_namespace = true
set {
name = "global.codefresh.accountId"
value = var.cf_account_id
}
set {
name = "global.codefresh.userToken.token"
value = var.cf_token
}
set {
name = "global.runtime.name"
value = "from-terraform"
}
}
You can get the values for both the Codefresh API token and account ID from the Codefresh UI as explained in the previous section.
The example is valid for the tunnel-based access mode. For ingress-based or service-mesh-based access modes, add the required arguments and values, as described in GitOps Runtimes with ingress controllers/service meshes.
Depending on your configuration, if you have private registries, you need to override specific image values, and if your Git servers are on-premises, you need to add custom repository certificates. See Optional GitOps Runtime configuration in this article.
By default, the GitOps Runtime can deploy to the cluster it is installed on. You can add Git Sources, use Terraform to connect external clusters, and create and deploy Argo CD applications.
Related articles
Configuring GitOps Runtimes
Upgrading GitOps Runtimes
Monitoring GitOps Runtimes
Managing GitOps Runtimes
Managing Git Sources in GitOps Runtimes
Managing external clusters in GitOps Runtimes