GitOps Runtime architecture
View components of GitOps Runtimes
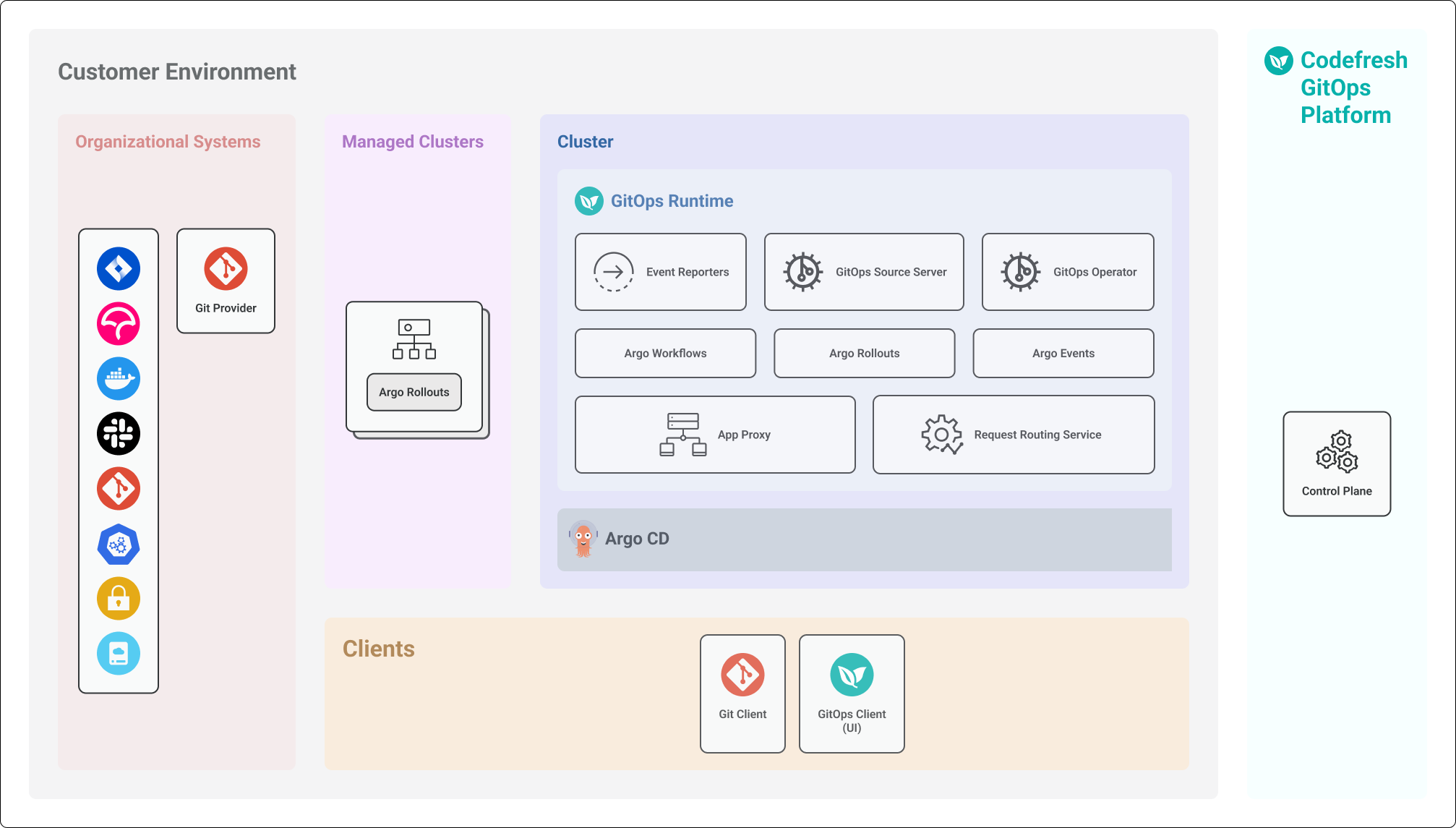
GitOps Runtime architecture overview
The GitOps Runtime in Codefresh provides the foundation for managing Argo CD applications using GitOps principles. It integrates with Argo CD to support continuous delivery, declarative deployments, and automated workflow execution.
Codefresh provides flexible installation options for the GitOps Runtime. You can install it alongside your existing Argo CD instance leveraging your current setup (bring your own Argo), or bundled with all the necessary Argo Project components, including Argo CD.
The GitOps Runtime always runs inside the customer’s cluster, regardless of the installation mode. See Runtime installation modes and architecture.
To optimize connectivity, the Runtime also supports different access modes, allowing communication through tunnelling or via an ingress controller. See Runtime access modes and architecture.
While the core components of the Runtime are the same for both installation and access modes, some components vary based on the access mode. See Runtime components.
Runtime installation modes and architecture
The GitOps Runtime is an Argo CD instance that runs inside your cluster. To accommodate organizations with or without an existing Argo CD instance, Codefresh supports two installation modes:
-
Runtime with an existing Argo CD instance
Integrates with an externally managed Argo CD instance. -
Runtime with a new Argo CD instance
Installs a dedicated Argo CD instance as part of the GitOps Runtime.
The primary architectural difference between these modes is the location of the Argo CD instance in relation to the GitOps Runtime.
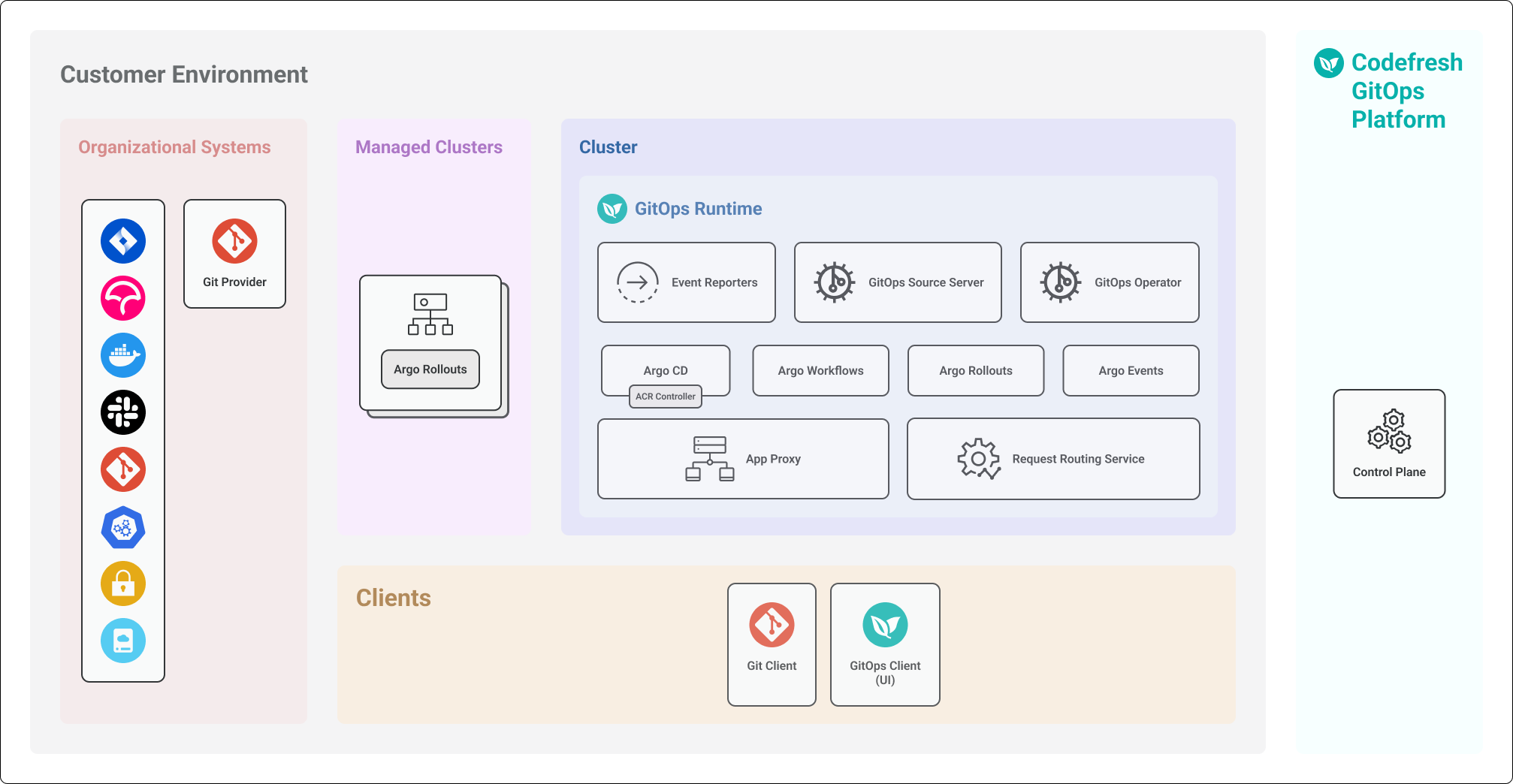
Runtime with existing Argo CD instance
In this installation mode, the GitOps Runtime integrates with an Argo CD instance that is already deployed and managed separately.
The Argo CD instance is within the same cluster as the GitOps Runtime but operates independently of it.
The Runtime authenticates with Argo CD and connects to key services to integrate GitOps capabilities.
Runtime with new Argo CD instance
In this installation mode, the GitOps Runtime includes a fully provisioned Argo CD instance as part of the installation. This provides a Runtime with all required GitOps components.
Core Runtime components
Regardless of the installation mode, the core Runtime components remain the same:
- Application Proxy
- Argo Project
- Event Reporters
- Source Server
- GitOps Operator
- Application Change Revision Controller
- Request Routing Service
Runtime access modes and architecture
Each installation mode supports two access modes, which determine how the GitOps Runtime in the customer’s cluster communicates with the Codefresh GitOps Platform.
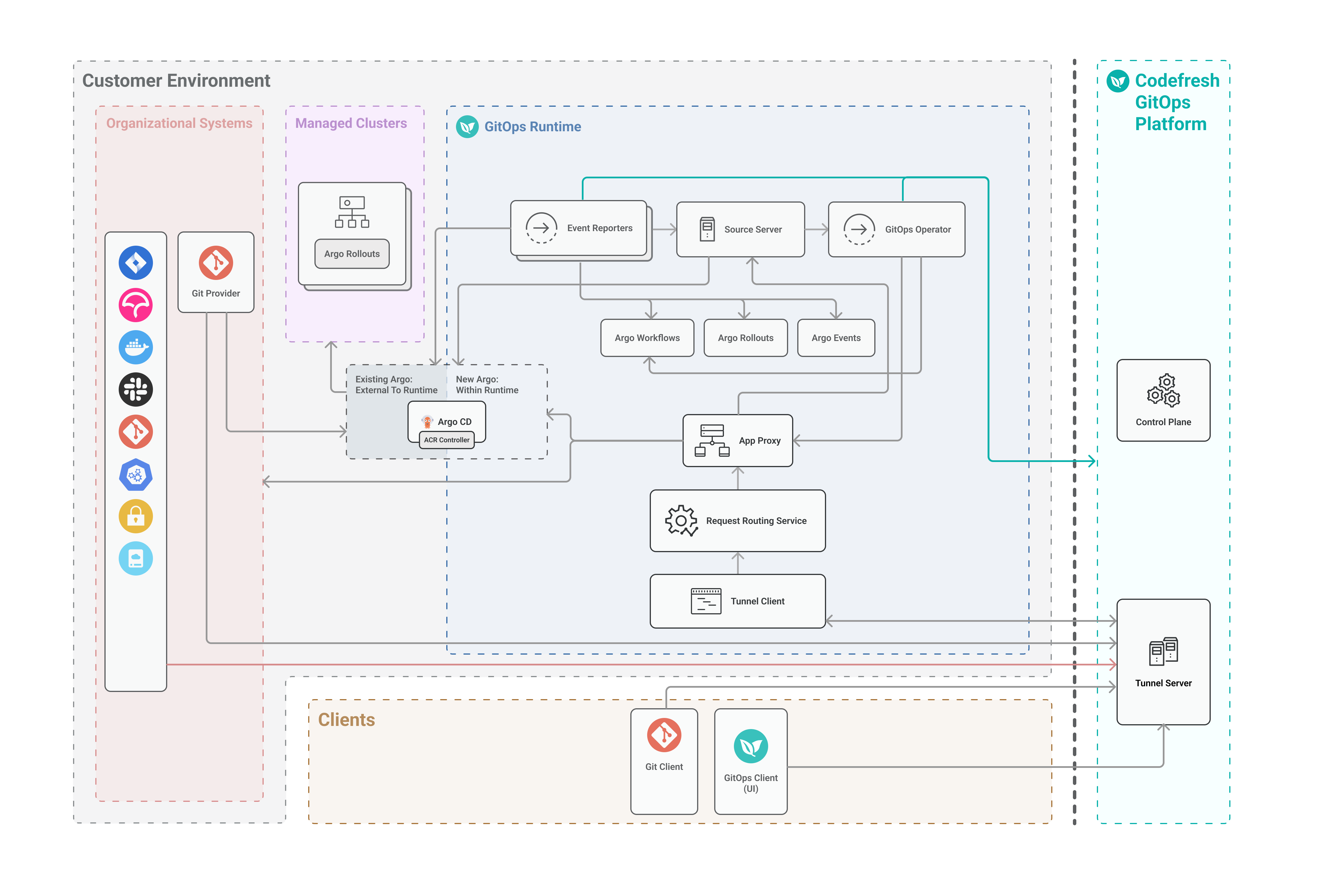
Tunnel-based access mode Runtime architecture
Tunnel-based access mode is the default access mode for GitOps Runtimes. Instead of using ingress controllers, this mode establishes a secure tunnel between the GitOps Runtime and the GitOps Platform.
Tunnel-based access modes are optimal when the cluster with the GitOps Runtime is not exposed to the internet.
This access mode includes two additional Runtime components:
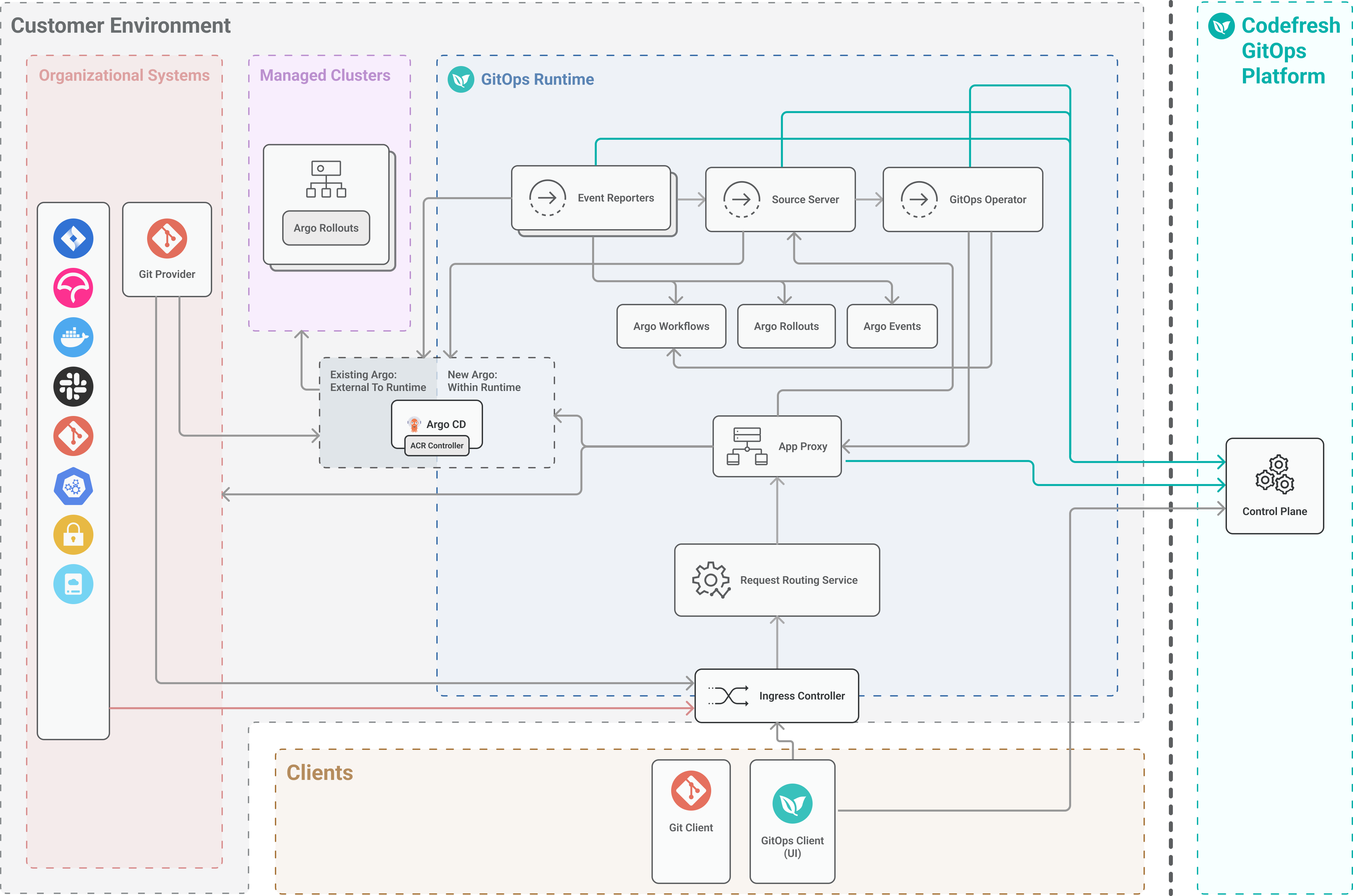
Ingress-based access mode Runtime architecture
Ingress-based access mode for GitOps Runtimes relies on ingress controllers to manage communication between the GitOps Runtime and the GitOps Platform.
Ingress-based access modes are optimal when the cluster with the GitOps Runtime is exposed to the internet.
Runtime components
The Runtime components differ depending on the access mode.
Application Proxy
The Application Proxy (App Proxy), functions as the Codefresh agent and is deployed as a service within the GitOps Runtime.
A key component of the GitOps Runtime, the App Proxy enables secure and reliable access to services running inside the cluster.
The App Proxy:
- Accepts and serves requests from GitOps Clients either via the UI or CLI
- Retrieves a list of Git repositories for visualization in the Client interfaces
- Retrieves permissions from the GitOps Control Plane to authenticate and authorize users for the required operations
- Implements commits for GitOps-controlled entities
- Implements state-change operations for non-GitOps controlled entities
App Proxy implementation depends on the access mode:
- Tunnel-based access mode: The Tunnel Client forwards the incoming traffic from the Tunnel Server using the Request Routing Service to the GitOps App Proxy.
- Ingress-based access mode: The App Proxy serves as the single point of contact between the GitOps Runtime, GitOps Clients, the GitOps Platform, and any organizational systems in the customer environment.
Argo Project
The Argo Project components include:
- Argo CD for declarative continuous deployment. The installation mode determines whether it runs within or outside the Runtime.
- Argo Rollouts for progressive delivery.
- Argo Workflows as the workflow engine.
- Argo Events for event-driven workflow automation framework.
To see which Argo Project component versions correspond to a Runtime version, see GitOps Runtime and Argo Project versions.
NOTE
Codefresh users rely on our platform to deliver software reliably, and predictably without interruption.
To maintain that high standard, we add several weeks of testing and bug fixes to new versions of Argo before making them available within Codefresh.
For Runtime installations with new Argo CD instances, typically, new versions are available in the GitOps Runtime within 30 days of their official release.
Event Reporters
Event Reporters monitor changes to resources deployed in the cluster and report them to the Codefresh platform.
Codefresh has two types of Event Reporters:
- Resource Event Reporter
- Application Event Reporter
Resource Event Reporter
The Resource Event Reporter monitors changes in their live-states of specific resource type, and sends the live-state manifests with the changes to Codefresh without preprocessing.
The Resource Event Reporter monitors live-state changes for:
- Rollouts (Argo Rollouts)
- ReplicaSets and Workflows (Argo Workflows)
Resource Event Reporters leverage Argo Event components such as Event Sources to monitor changes to the live-state manifests, and Sensors to send the live-state manifests to Codefresh. For setup information on these Argo Event components, see Argo CD’s documentation on Event Source and Sensor.
Application Event Reporter
The Application Event Reporter monitors changes to Argo CD applications deployed in the cluster, and reports these changes to Codefresh.
Unlike the Resource Event Reporter which utilizes Argo Events, the Application Event Reporter:
- Uses a proprietary implementation with an event queue to process application change-events and sharding for a robust and scalable setup.
- Retrieves both the live-state manifest of the application, and the Git manifests for all the application’s managed resources.
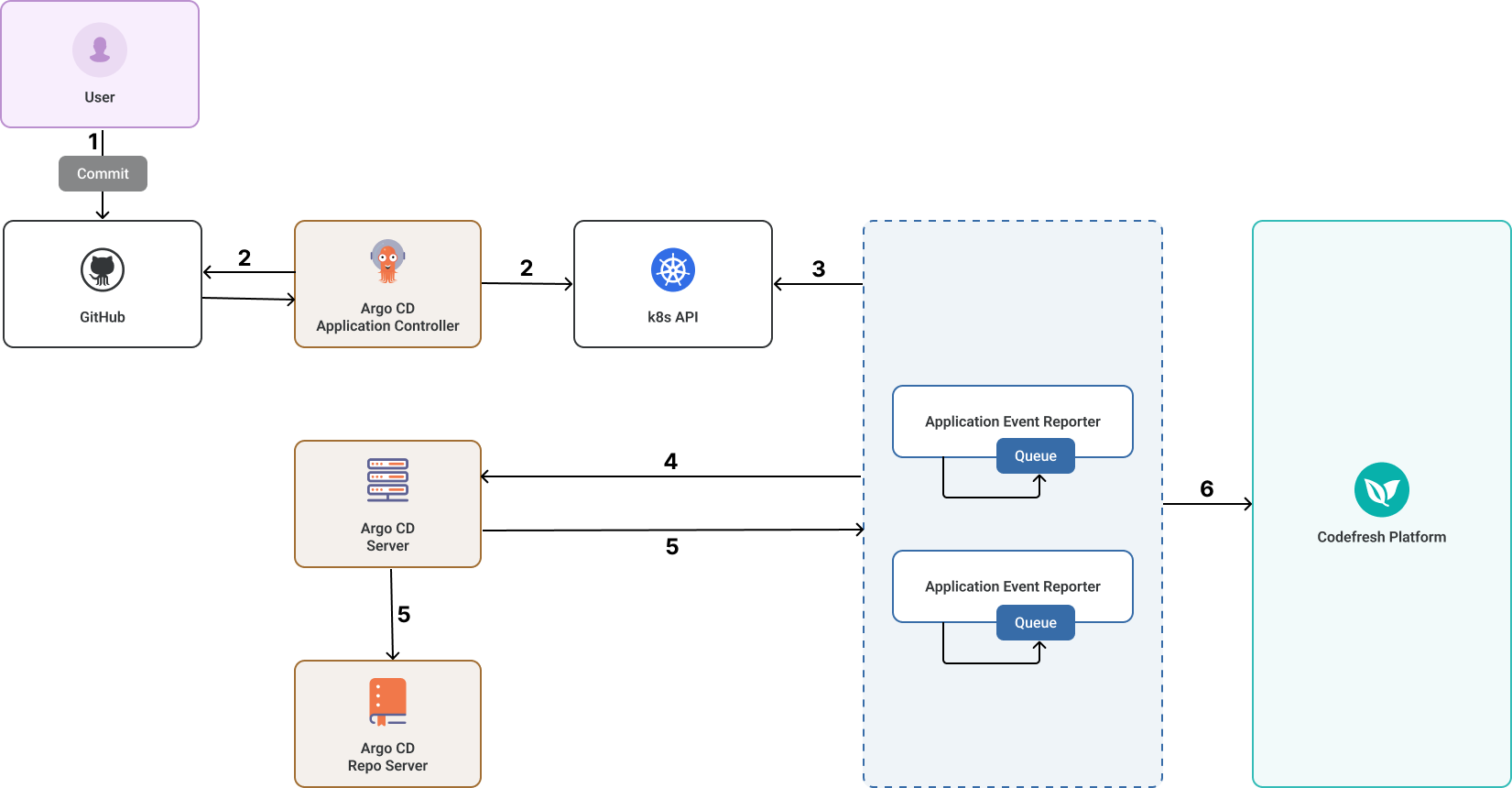
Application Event Reporter data flow
The diagram below illustrates the data flow for the Application Event Reporter (identified in the cluster as event-reporter):
-
The user makes changes to the application manifest or its managed resources and commits them to the Git repository.
-
The Argo CD Application Controller monitors the Git repository for changes, synchronizes the updates with the cluster, and forwards the changes to the Kubernetes API.
-
The Application Event Reporter subscribes to the Kubernetes API to receive application-change events.
- If there are multiple instances of the Application Event Reporter, each instance subscribes to a set of specific applications determined through a hash function on the application name.
- The application-change event is added to the Event Queue of the appropriate Application Reporter instance for processing based on the shard to which it belongs. Each instance of the Application Reporter can queue up to 1,000 events at a time.
NOTE
The number of Application Event Reporters are equal to the configured number of replicas. By default, there are five replicas, but the number can be customized through theargo-cd.eventReporter.replicasparameter in your Helm values file values.yaml.
-
The Application Event Reporter requests both the application’s live-state manifest and the Git manifests for all the application’s managed resources from the Argo CD Server.
-
The Argo CD server retrieves these manifests from the Argo CD repo-server and forwards them to the Application Event Reporter.
-
The Application Event Reporter reports the application-change events to the Codefresh platform.
Source Server
The Source Server retrieves Git manifest and revision data from Argo CD upon request from the Event Reporters or App Proxy. This ensures that GitOps operations always use the latest data.
GitOps Operator
The GitOps Operator manages:
- Resources for Restricted Git Sources
- Orchestrates promotions It interacts with Argo Workflows, App Proxy, and the Codefresh platform to ensure seamless promotion execution and governance.
Application Change Revision Controller
The Application Change Revision (ACR) Controller is a Codefresh-specific component integrated into Argo CD. Its primary function is to identify and display the exact revision associated with an application change that triggered a promotion or deployment in monorepo environments.
In monorepo environments where multiple applications share a single repository, the ACR Controller:
- Detects and associates the precise revision responsible for triggering a promotion or deployment of a specific application.
- Ensures that notifications are scoped to the application that was actually modified, preventing unnecessary notifications for other applications within the same repository, improving clarity and reducing noise.
NOTE
The ACR Controller is supported from Runtime version 0.13.0 and higher for GitOps Runtime installations with new Argo CD. Not supported for installations with existing Argo CD.
It does not support multi-source applications.
Configuration
The ACR Controller must be explicitly enabled in the argo-cd section of the Runtime’s values.yaml file. See Enable precise sync detection for monorepo apps.
Request Routing Service
The Request Routing Service is installed in the same cluster as the GitOps Runtime, and:
- Receives requests from the Tunnel Client (tunnel-based) or the ingress controller (ingress-based)
- Forwards the request URLs to the Application Proxy, and webhooks directly to the Event Sources
IMPORTANT
The Request Routing Service is available from Runtime version 0.0.543 and higher.
Older Runtime versions are not affected as the ingress controller continues to route incoming requests and there is full backward compatibility.
Tunnel Server (Tunnel-based Runtimes only)
The Tunnel Server is installed in the Codefresh platform. It communicates with the enterprise cluster located behind a NAT or firewall.
The Tunnel Server:
- Forwards traffic from Codefresh Clients to the client (customer) cluster.
- Manages the lifecycle of the Tunnel Client.
- Authenticates requests from the Tunnel Client to open tunneling connections.
Tunnel Client (Tunnel-based Runtimes only)
Installed on the same cluster as the GitOps Runtime, the Tunnel Client establishes the tunneling connection to the Tunnel Server via the WebSocket Secure (WSS) protocol.
A single GitOps Runtime can have a single Tunnel Client.
The Tunnel Client:
- Initiates the connection with the Tunnel Server.
- Forwards the incoming traffic from the Tunnel Server through the Request Routing Service to App Proxy, and other services.
Customer environment
The customer environment that communicates with the GitOps Runtime and Codefresh generally includes:
- Ingress controller for ingress-based GitOps Runtimes
The ingress controller is configured on the same Kubernetes cluster as the GitOps Runtime, and implements the ingress traffic rules for the GitOps Runtime. See Ingress controller requirements. - Managed clusters
Managed clusters are external clusters registered to provisioned GitOps Runtimes for application deployment.
Hybrid GitOps allow you to add external clusters after provisioning the Runtimes.
See Managing external clusters in GitOps Runtimes. - Organizational Systems
Organizational Systems include the customer’s tracking, monitoring, notification, container registries, Git providers, and other systems. They can be entirely on-premises or in the public cloud.
Either the ingress controller (ingress-based access mode), or the Tunnel Client (tunnel-based access mode), forwards incoming events to the Application Proxy.
Data flow: GitOps Runtime & external systems
The GitOps Runtime interacts with external systems and components in the customer environment to enable GitOps operations and processes.
- Runtime cluster
- Both Argo CD and Codefresh components within the Runtime interact with the Runtime cluster’s Kubernetes API server.
- Argo CD components also access managed clusters registered to GitOps Runtimes to deploy applications.
- Git providers
- Argo CD components access Git providers such as GitHub. Git provider credentials are always securely stored in the customer’s cluster.
- Codefresh components also access the Git provider to enable UI-driven commits and pull requests.
- Container registries and Jira (optional)
If enrichment functionality is enabled, jobs can be executed within the Runtime cluster or a CI system to retrieve metadata from those container registries and Jira instances integrated with Codefresh.
Data reporting: GitOps Runtime to Codefresh Platform
The GitOps Runtime reports data to the Codefresh platform, which stores the data.
| Entity/Metadata | Reported data |
|---|---|
| Kubernetes resources |
|
| Git commit metadata |
|
| Jira issue metadata |
|
| Docker image metadata |
|
Related articles
Install GitOps Runtime with existing Argo CD
Install GitOps Runtime with new Argo CD